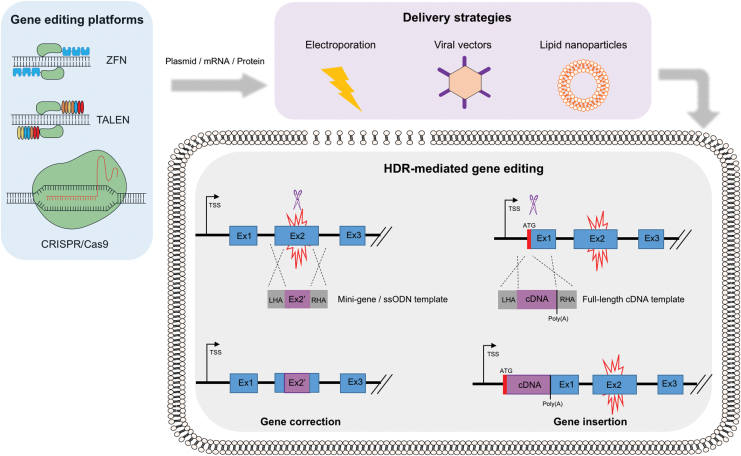
Figure 1.
HDR-mediated genome editing strategies to achieve physiological expression of the correct gene. Gene editing platforms, such as ZFNs, TALENs, and CRISPR/Cas9, are delivered to the target cell in either a plasmid, RNA, and/or protein format (blue box). Strategies to introduce these reagents into the cells include electroporation, viral vectors, and lipid nanoparticles (purple box). Once the endonucleases reach the cell nucleus, upon binding to the DNA, they induce double-strand breaks (blue scissors) at specific sites. Two major HDR-based strategies can be implemented to revert a disease phenotype caused by a genetic mutation (red spark), while preserving endogenous regulation and wild-type levels of expression of the correct protein. In the case of gene correction, the delivery of a mini-gene or a ssODN donor template can replace small fragments of the mutated region or correct a few base-pair mutation. In the case of gene insertion, a wild-type cDNA donor template can be knocked-in close to or in frame with the translation start codon (ATG) of the mutated gene. Both strategies will result in the functional restoration of regulated and physiological protein expression, driven by endogenous transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulatory regions. CRISPR/Cas9, clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats/associated Cas9 nuclease; HDR, homology directed repair; ssODN, single-strand oligo DNA; TALEN, transcription activator effector nuclease; ZFN, zinc finger nuclease. Color images are available online.