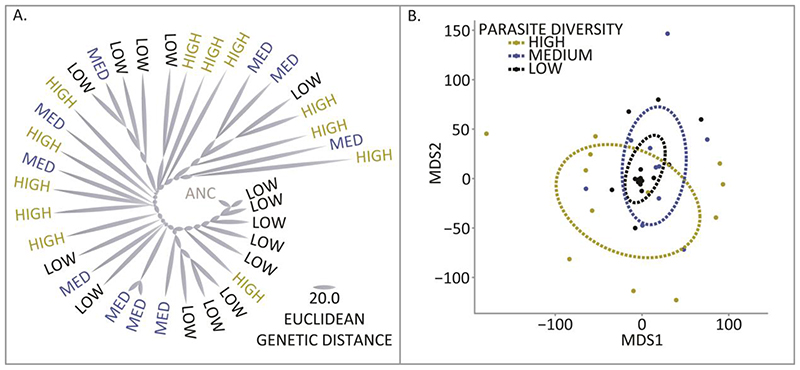
Fig. 2. Parasite diversity accelerates host evolution.
(A) Host allele frequencies after 10 days of coevolution from the high (yellow), medium (blue) and low (black) parasite diversity treatments were used to calculate pairwise Euclidean distances between the ancestral sequence (grey) and each coevolved population. Increasing parasite diversity accelerated the rate of host evolution. (B) The genetic distances between coevolved populations were ordinated by non-metric multidimensional scaling. The ellipses represent a 95% confidence bubble around the means for the different treatments. We found evidence of divergence between populations within treatments (ANOSIM R = 0.11 P < 0.01), and the greatest within treatment diversification was observed in the high parasite diversity treatment.