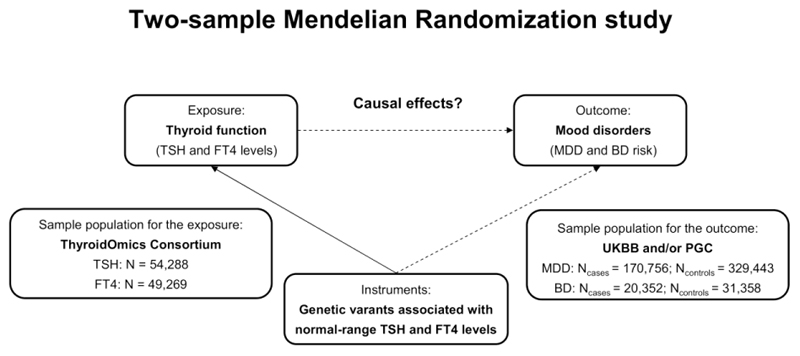
Figure 1. Schematic diagram illustrating the study design.
Two-sample Mendelian Randomization (MR) approach based on the summary-level data from large-scale meta-analyses of the genome-wide association studies (GWAS) was used to investigate the causal effects of thyroid function on mood disorders. Genetic variants associated with normal-range TSH and FT4 levels (genetic instruments, represented by the solid line) and their corresponding effect estimates were established in the GWAS by the ThyroidOmics Consortium (35). Effect estimates on major depressive disorder (MDD) and bipolar disorder (BD) for these genetic variants were derived from the GWAS in the UK Biobank (UKBB) and/or the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium (PGC) (36–38). All datasets used in this study are publicly available at the ThyroidOmics Consortium and the PGC websites.