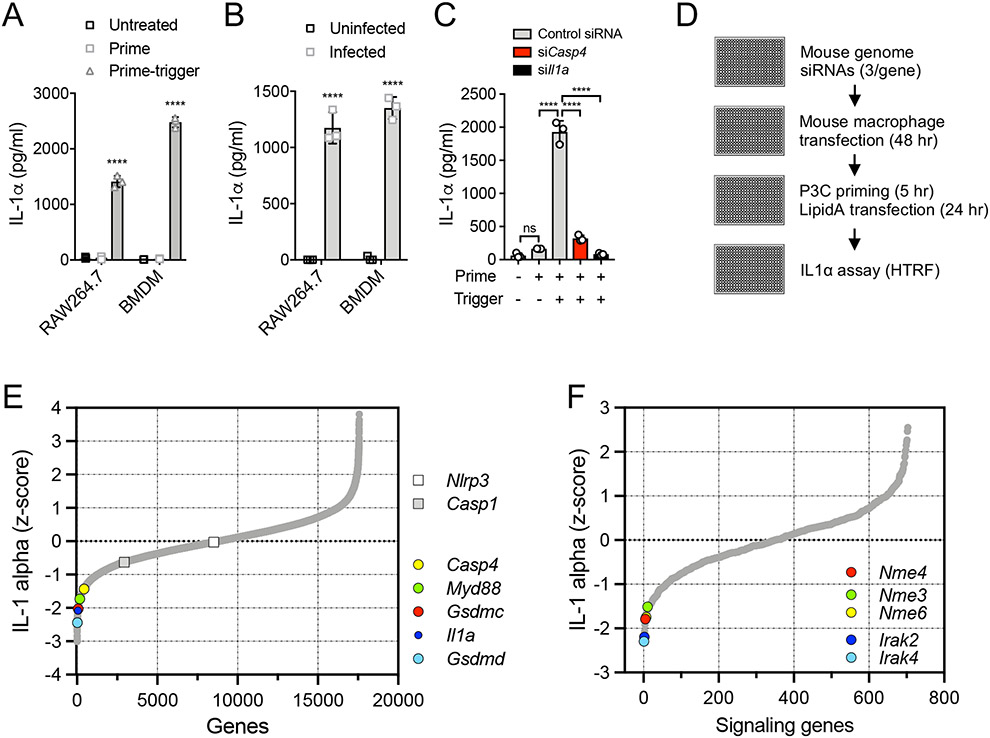
Figure 1: A genome-wide RNAi screen identifies mitochondrial Nme genes as positive regulators of the non-canonical inflammasome.
(A) RAW264.7 cells and BMDM were primed with 100 nM or 1 μg/ml P3C (respectively) for 5 hr and triggered by 100 nM LipidA transfection for 18 hr. Secreted IL-1α was measured by ELISA. (B) RAW264.7 cells and BMDM were infected with B. cenocepecia (MOI 10) for 18 hr. Secreted IL-1α was measured by ELISA. (C) RAW264.7 cells, transfected with non-targeting control, Il1a or Casp4 siRNA, were primed and triggered as in (A). (D) Arrayed siRNA screen workflow. (E) Phenotypic distribution of the genome-wide screen highlighting known inflammasome components. (F) Phenotypic distribution of a pilot set of signaling genes showing Irak4 and Irak2 as a expected priming-dependent hits, and identification of the Nme genes as a positive regulators of prime-trigger-induced IL-1α release. (A-C) Data are representative of three independent experiments and expressed as mean ± SD, (n=3); (A, B) Two-Way ANOVA and (C) One-Way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test; (A, B) untreated vs. treated cells; ****p < 0.0001.