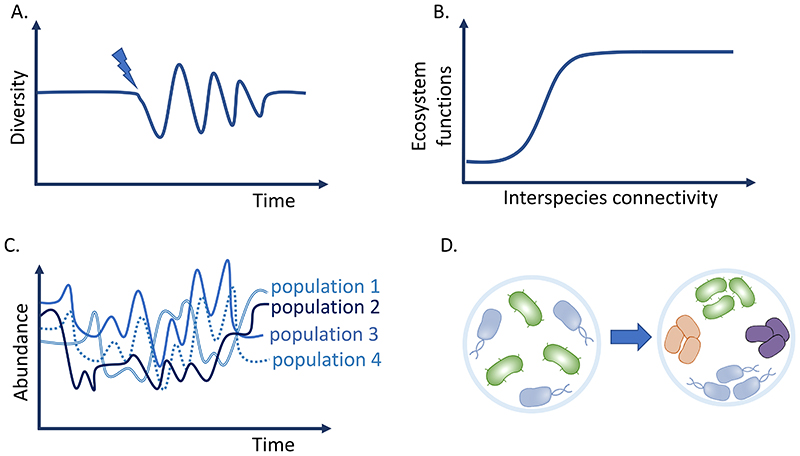
Figure 1. Examples of emergent properties arising from community complexity.
A. Stability and resilience. Interactions among community members can buffer against biotic and/or abiotic perturbations leading back to stable compositional state [82, 113, 136]. Blue arrow indicates a perturbation event. B. Phenotypes. Emergent functions such as substrate utilization, biomass production, cross-protection, result from the cooperation between community members. [104, 110, 139]. C. Persistence. Strains that would otherwise face competitive exclusion can coexist via, for instance, the intermediary of a cross-fed metabolite secreted by another community member [84, 88, 175]. D. Self-organisation. Balance between competitive and cooperative interactions can lead to spatial patterning, such as the formation of clonal patches [30, 47, 141].