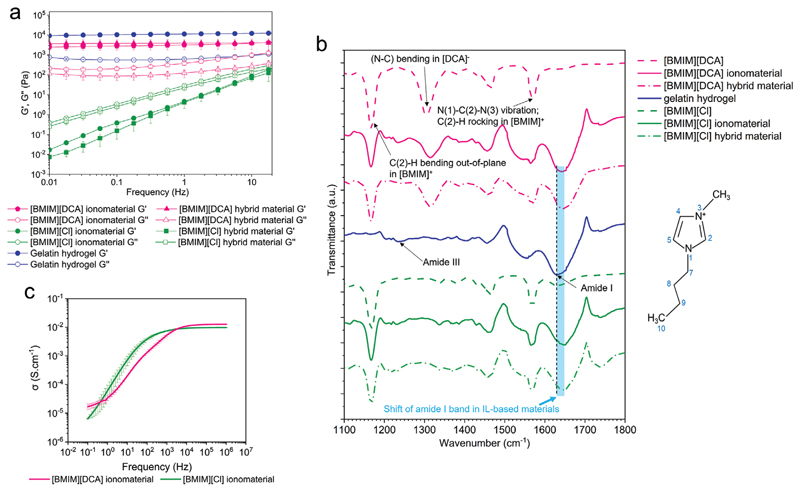
Figure 2. Characterization of gelatin ionomaterials and hybrid materials.
a) Viscoelastic properties (shear storage (G′) and loss (G″) moduli) of hybrid materials composed of gelatin, 5CB, water, and either [BMIM][DCA] or [BMIM][Cl], respective ionomaterials and gelatin hydrogel (n = 3). b) Details of ATR-FTIR spectra in the amide region. The blue shaded area indicates the shift of the gelatin amide I band (C═O) to higher frequencies in the ionomaterials and hybrid materials compared to the hydrogel. The numbering of carbon and nitrogen atoms is represented near the [BMIM]+ structure to ease the interpretation of the spectra. c) Ionic conductivity of [BMIM][Cl]- and [BMIM][DCA]-based gelatin ionomaterials at room conditions (51% RH) (n = 2).