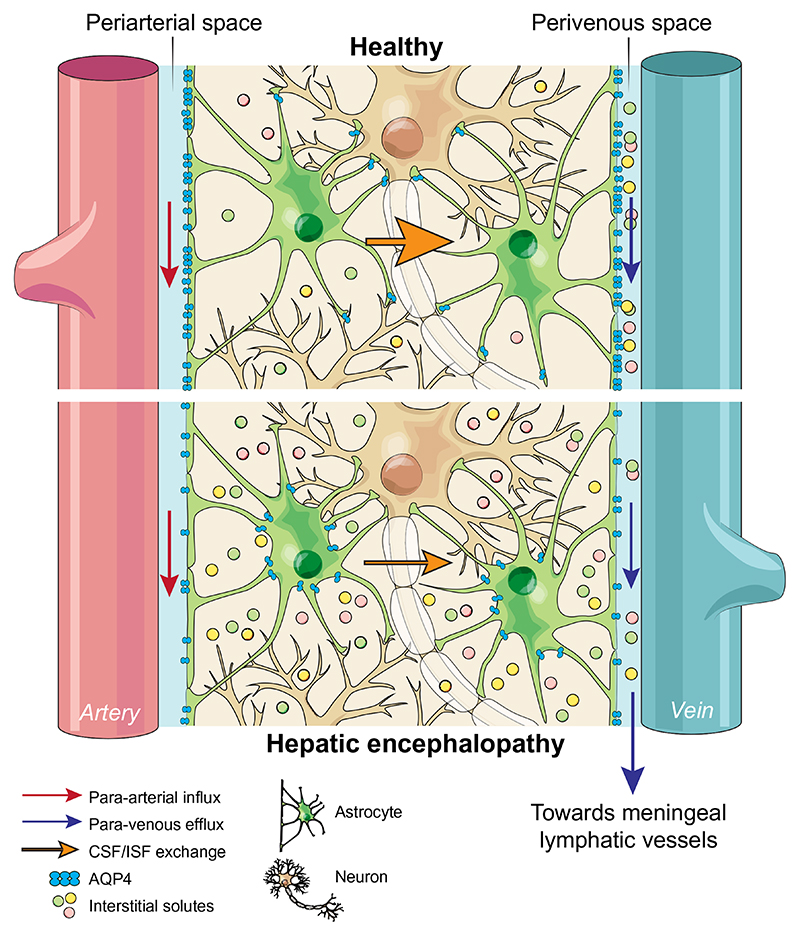
Fig. 1. Schematic of proposed alterations in glymphatic function in hepatic encephalopathy.
In health, glymphatic inflow of CSF occurs parallel to arterial flow along the periarterial space (between the basement membrane of smooth muscle cells and pia mater), where the water component of CSF crosses the astrocytic AQP4 channels polarised to astrocyte end-feet and enters the brain parenchyma. Here, CSF exchanges with ISF, allowing interstitial solutes to be cleared out of the parenchyma via astroglial transporters or channels, or pass through the astrocytic end-feet clefts to the perivenous space. Effluxed waste is then cleared out of the CSF pool via absorption by the meningeal lymphatic system. In hepatic encephalopathy, our data suggests that this brain-wide clearance system becomes dysfunctional, possibly because of reduced vessel coverage and polarisation of AQP4, leading to toxic accumulation of interstitial solutes in the parenchyma. Arrows indicate direction of flow. AQP4, aquaporin-4; CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; ISF, interstitial fluid.