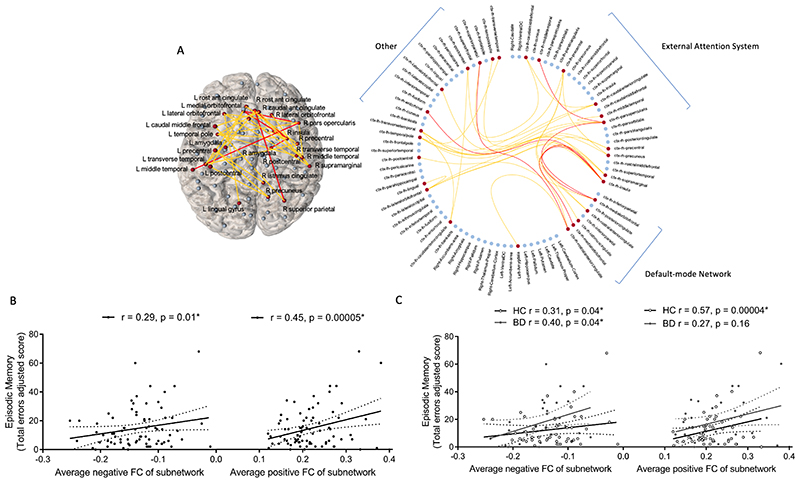
Figure 2.
A resting-state functional subnetwork (Pearson-correlation-derived networks) was correlated with episodic memory total errors over all subjects covarying for age, gender and diagnosis (T = 3, p = 0.02), while no subnetwork differently related to this measure between diagnostic groups: (A) Visualisation of significant subnetwork in anatomical space and a circular representation including all network nodes. Positive functional connections are coloured yellow, negative functional connections are coloured red and brain regions in the significant subnetwork are coloured red. In order to compare to previous literature brain regions are ordered according to networks defined using independent component analysis as per Fornito et al. (2012). (B) Relationship between average positive and average negative functional connectivity of this subnetwork and episodic memory total errors in the overall sample and (C) separated by diagnostic group, with partial correlations including age and gender as covariates. HC, healthy control; BD, bipolar disorder.