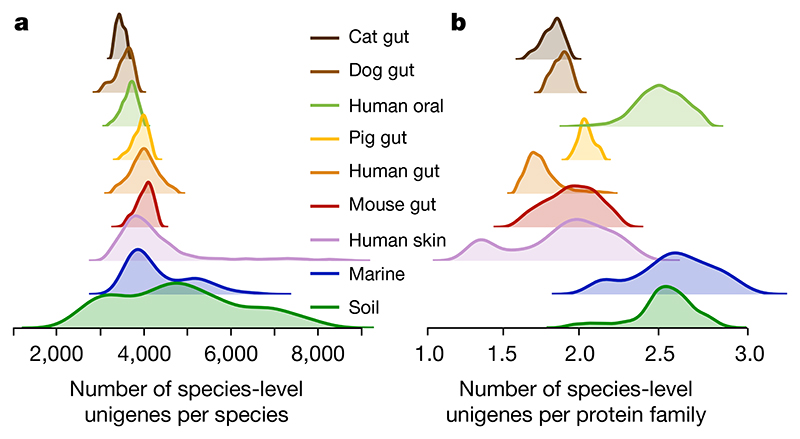
Fig. 2. The number of conspecific genes (gene pool per species) and the functional redundancy in each metagenome show significantly less variation within than between habitats.
a, Density (smoothed histogram using a Gaussian kernel with the width automatically determined (Methods)) of the number of conspecific genes in each sample, by habitat, shows that the largest per-sample pangenomes are present in environmental samples rather than in host-associated habitats. b, Density of the number of unigenes for each protein family (a proxy for functional redundancy) detected in each sample, per habitat, shows clear differences between habitats. The protein family richness is highly correlated in the well-studied human gut habitat to the stricter orthologue-richness estimate obtained using eggnog-mapper217 and extends to all habitats (Methods).