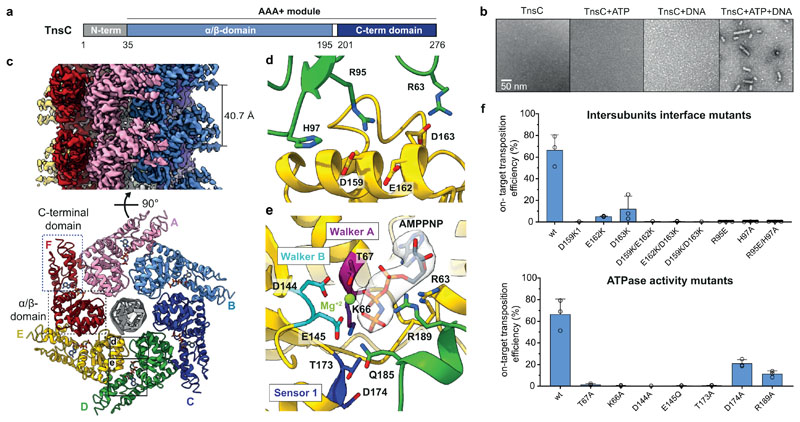
Fig. 2. Cryo-EM structure of the ShTnsC-AMPPNP-dsDNA filaments.
a, Domain organization of ShTnsC. b, Representative negative stain electron micrographs of ShTnsC incu the presence or absence of dsDNA and/or ATP. Magnification, 68,000 x. Experiment was repeated two times independently with similar results. c, Cryo-EM density map and structural model of the dsDNA- and AMPPMP-bound ShTnsC filament at 3.6 Å overall resolution (side and top views). Protein subunits are uniquely colored. dsDNA is shown in grey. d–e, Detailed views of the inter-protomer interface and of the ATPase catalytic site. Density corresponding to AMPPNP is shown (contour level of 4.0 σ). f, Site-specific transposition activity in E. coli of ShCAST systems containing mutations at the inter-protomer interface and in the catalytic pocket of ShTnsC, as determined by droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) analysis. Data are presented as mean ± s.d. (n=3 biologically independent replicates).