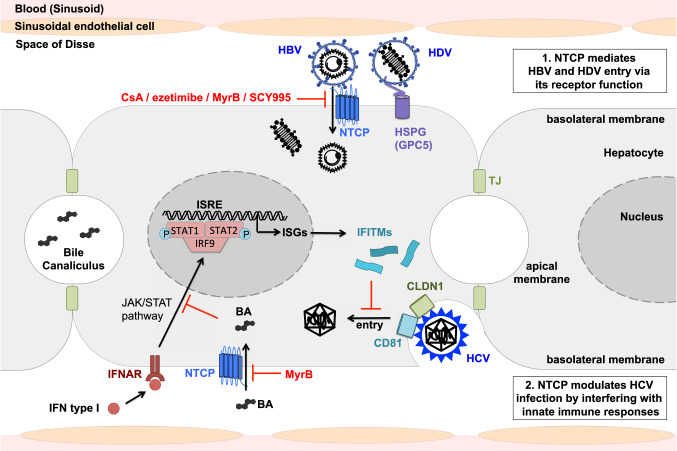
Fig. 2.
Model of interactions between NTCP and the entry of HBV, HDV, and HCV in hepatocytes. After initial attachment to HSPG including GPC5, HBV and HDV virions bind to the receptor NTCP through the preS1-domain of the large envelope protein. NTCP inhibitors CsA and ezetimibe block viral entry like preS1-derived MyrB and CsA-derived SCY995. NTCP modulates HCV infection by interfering with innate immune responses. Bile acids interfere with the IFN signaling pathway and thereby favor HCV entry. Inhibition of NTCP-mediated bile acid import into hepatocytes promotes inhibition of HCV entry through the upregulation of ISGs including IFITMs. HBV hepatitis B virus, HCV hepatitis C virus, HDV hepatitis D virus, HSPG heparan sulfate proteoglycan, GPC5 glypican-5, NTCP sodium taurocholate co-transporting polypeptide, MyrB myrcludex B, CsA cyclosporin A, SCY995 synthesized CsA derivative 995, IFN interferon, IFNAR IFN-α/β receptor, JAK Janus kinase, STAT signal transducer and activator of transcription, IRF9 Interferon regulatory factor 9, ISRE IFN-sensitive response element, ISG IFN-stimulated gene, IFITM IFN-induced transmembrane protein, CLDN1 Claudin 1, CD81 cluster of differentiation 81, BA bile acid, TJ tight junction