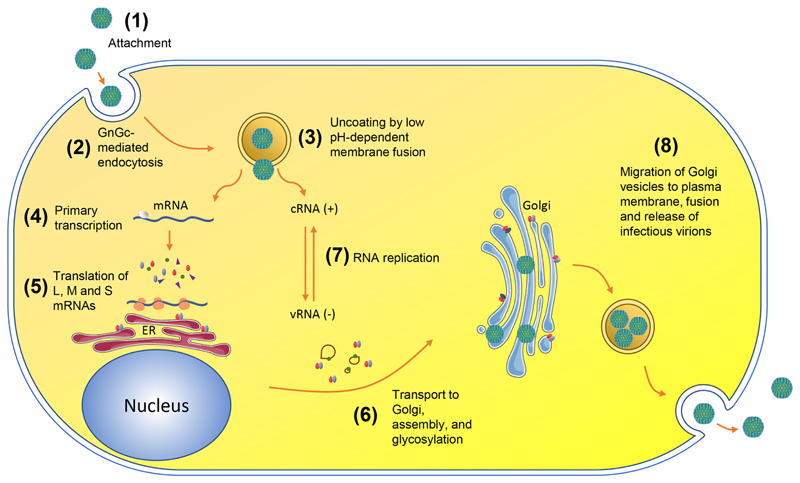
Fig. 4.
Replication cycle of RVFV. (1) Viral attachment to host membrane. (2) GnGc-mediated endocytosis. (3) Uncoating by acidification of endocytic vesicles, fusion of viral and endosomal membranes. (4) Primary transcription of mRNA by viral RNA polymerase. (5) Translation of viral proteins, cleavage of M-segment polyprotein and dimerization of GnGc in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). (6) Transportation of GnGc hetrerodimers to the Golgi, glycosylation of Gn and Gc and budding into the Golgi cisternae. (7) RNA replication into positive-sense complimentary RNA (cRNA), which serves as a template for negative-sense viral RNA (or in the case of the ambisense S segment, templates for sub-genomic mRNA). (8) Migration of Golgi vesicles containing viruses to cell surface, fusion of vesicular membranes with plasma membrane, release of infectious virions. Adapted from [87]. Permission was obtained to adapt the figure from the authors and the copyright holder.