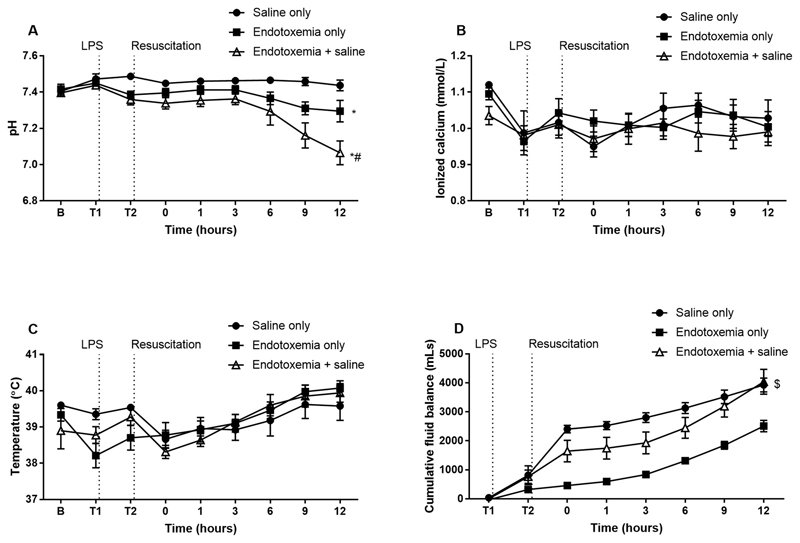
Fig. 2.
The effect of saline resuscitation on physiological parameters. Endotoxemia + saline altered pH (A) compared to endotoxemia only while there was no change in ionized calcium (B) or body temperature (C). There was a significant increase in the volume of fluid administered during resuscitation for saline only and endotoxemia + saline animals (D). Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.01 versus saline only; #p < 0.05 versus endotoxemia only; $p < 0.05 versus endotoxemia only. n = 5 saline only, n = 8 endotoxemia only, n = 8 endotoxemia + saline. LPS = lipopolysaccharide; B = baseline.