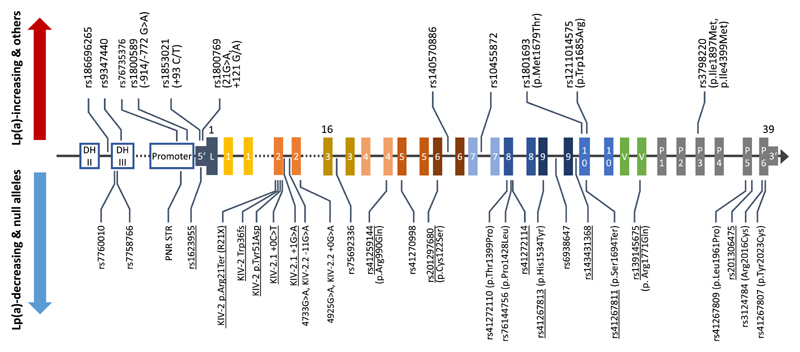
Fig. 3. Location of relevant LPA SNPs.
Location of multiple LPA SNPs with remarkable effects that have been discussed in the literature. Table 1 provides background information. The exons are numbered according to the domain that they encode (1-10: KIV-1 to KIV-10, L. leader sequence, P. protease domain, 5’: 5’UTR, 3’: 3’ UTR). For orientation, some exons carry a superscript reporting the exon number in the genome sequence hg38. SNPs that have been associated with increased Lp(a) concentrations or that act through other mechanisms (rs1211014575, which prevents OxPL binding) are shown above the gene structure; SNPs that have been associated with decreased Lp(a) (both causally or by association only) are shown below. SNPs that cause null alleles are underlined, albeit many more Lp(a)-lowering SNPs may cause null alleles if occurring on an allele with already low Lp(a) production. SNPs in the KIV-2 are named according to their publication, as they cannot be assigned a single rs-identifier because their location is not unique. Gene structure is not in scale.