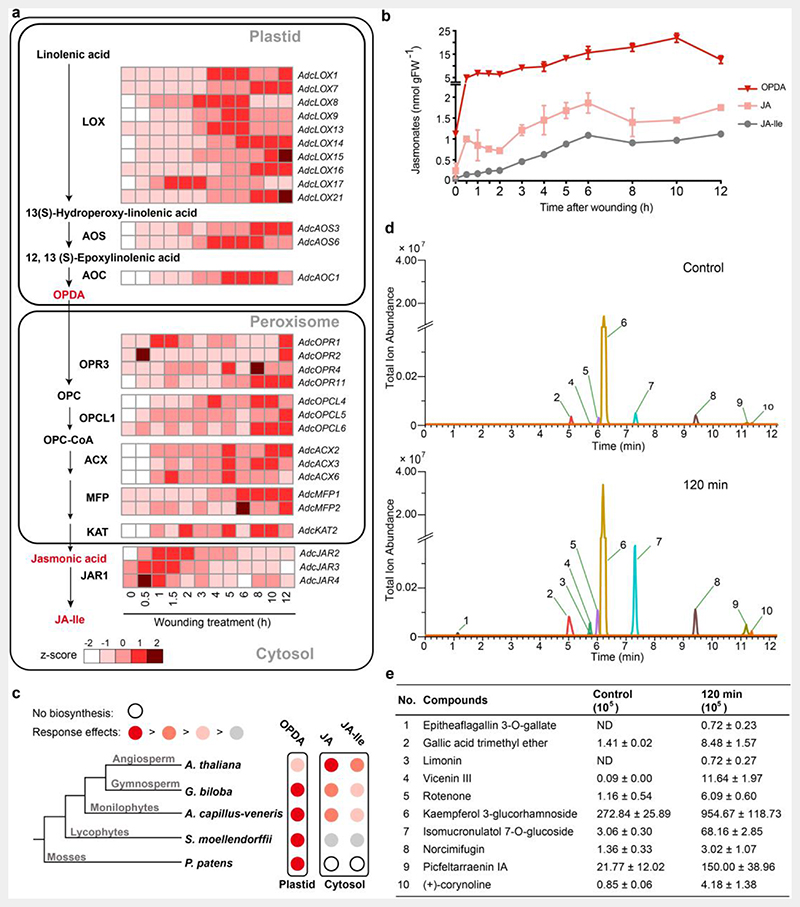
Fig. 4. Jasmonate biosynthesis pathway and defense-related metabolites in A. capillus-veneris.
a. Jasmonate (JA) biosynthesis pathway and expression profile of the representative genes. The fragments per kilobase per million mapped reads (FPKM) were used to evaluate the expression of each gene, during seven developmental phases, and after a mechanical wounding treatment.
b. Time course of the mechanical wound response of JA (the precursor OPDA, jasmonic acid, and JA-Ile). Pinnae were wounded with a hemostat. Damaged pinnae were harvested at the indicated time points after wounding and analyzed for jasmonates accumulation by high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS); each data point represents the mean ± SD of five biological replicates.
c. Schematic diagram showing the relative increases in each jasmonate after mechanical wounding in species from five major clades of land plants. The relative response effects of OPDA, jasmonic acid, and JA-Ile are compared in each species, with data reported in references for P. patens, S. moellendorffii, and Arabidopsis and data generated in this study (A. capillus-veneris and G. biloba). The major jasmonate molecule exhibiting a rapid increase and considerable accumulation is indicated in dark red. The second effective wound response jasmonate with a rate and accumulation comparable to those of the major jasmonate molecule is indicated in red. The jasmonate with wound response biosynthesis is weaker and slower than that of the major jasmonte is indicated in pink. The jasmonate with wound response biosynthesis is far weaker (smaller than 100 times) than that of the major JA is indicated in gray. In P. patens, the biosynthesis of jasmonic acid and JA-Ile is absent, as indicated by an open circle.
d. Extracted ion chromatograms (EICs) showed coronatine-induced significant changes of metabolites with defense function in ferns. Metabolites of fern leaves treated with coronatine for 2 h were measured using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole/mass spectrometry (UHPLC-QE/MS), with leaves without treatment as a control. Metabolites with well-known insect resistance functions that were significantly enriched in the 2-h samples were extracted and labeled; metabolites labeled 1-10 are named in (e).
e. Abundance of significantly enriched defense-related compounds labeled 1-10 in (d). The values are expressed as means ± SD (n = 5 independent biological samples). ND, not detected. Detailed data are provided in Extended Data Table 6.