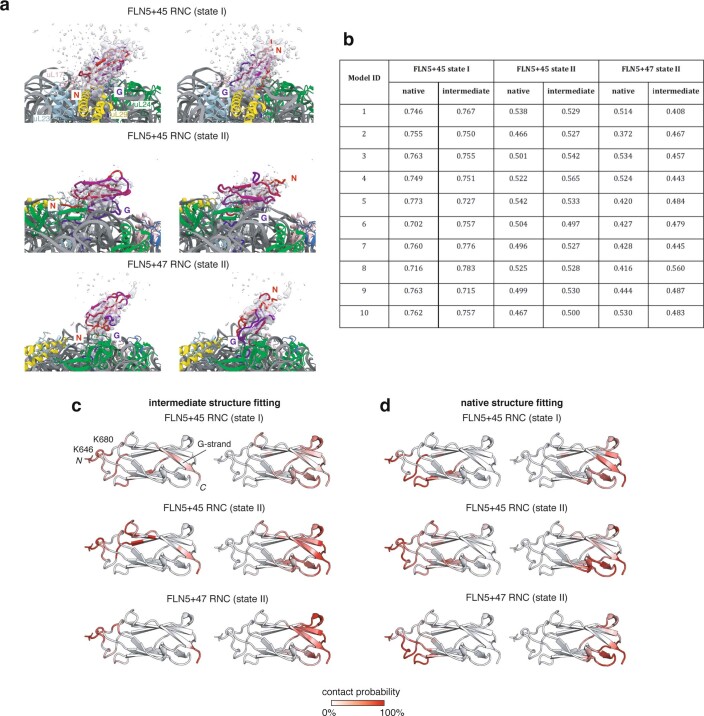
Extended Data Fig. 8. Models of the co-translational intermediates of FLN5 by all-atom, cryo-EM density-driven MD simulations.
a, Examples of structural models of FLN5 co-translational intermediates fitted to previously obtained cryo-EM densities of FLN5 + 45 and FLN5 + 47 RNCs31. Two major orientations are observed, in which the N-terminus of the FLN5 domain points towards (left) or away (right) from the ribosome. The FLN5 domain is coloured from its N- (red) to C-terminus (blue), with its N-terminus (N) and G-strand labelled (G). Cryo-electron densities are shown in grey, and at a contour level of two sigma. b, Cross-correlation values for cryo-EM density-guided MD simulations of native and intermediate state RNCs. For each of the 10 density-guided simulations obtained using the three electron density maps31, we generated final models for the intermediate state, from which electron density maps were simulated and compared against the nascent chain experimental maps. The resulting cross-correlation values, calculated as in ChimeraX65, for the intermediate state are shown alongside cross-correlations using the same approach as previously for the native state (Javed et al, submitted). c, Contact probabilities of FLN5 residues with the ribosome surface by analysis of models of the intermediate as shown in a for the two main orientations observed (N-terminus of FLN5 towards and away from the ribosome, left and right, respectively). Regions of highest contact probability, residues K646 and K680 and G-strand, labelled. d, As in b, but for models of the native state from previous all-atom cryo-EM density-driven MD simulations using the same cryo-EM map31.