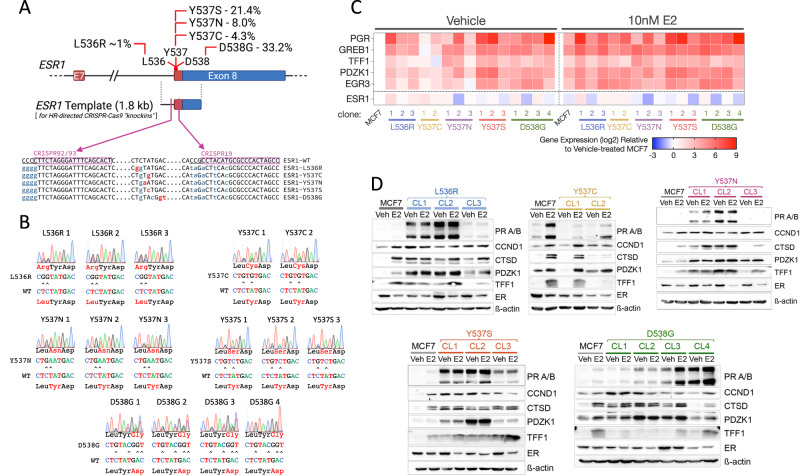
Fig. 1. CRISPR-Cas9-directed generation of mutations in the ESR1 gene in MCF7 breast cancer cells.
A The schematic outlines the strategy used to generate mutations in the endogenous ESR1 gene in MCF7 cells. The percentages refer to the prevalence of the different mutations in metastatic breast cancer patients, as described [42]. Shown are the positions of the CRISPR sequences, with PAM sequences underlined. Base changes introduced in the ESR1 template are shown in lower case, mutations in red being ones that change the amino acid and silent mutations in the CRISPR targeting/PAM sites shown in orange. B Shown are sequencing chromatograms for DNA prepared from each ESR1 mutant clone. C RNA was prepared from cells cultured in the absence of estrogen and treated with 10 nM estrogen for 16 h (n = 3). Gene expression was normalised to expression of the housekeeping gene TBP. The heat map shows the mean gene expression relative to expression in estrogen-free MCF7 cells. D Protein lysates were prepared as in (C). The immunoblotting panels show the results of one representative experiment. The same MCF7-WT lysates were used in each panel, for comparison across the different mutations (Supplementary Fig. 2 shows quantification of the 3 independent replicates.