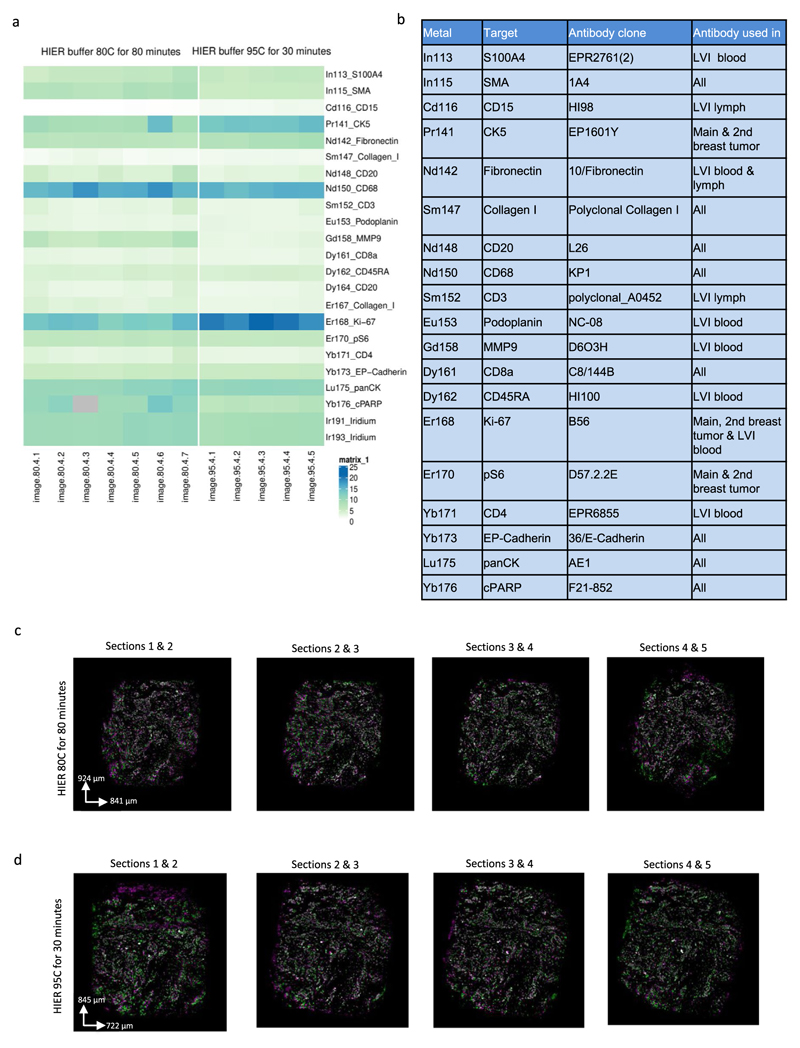
Extended Data Fig. 1. A comparison of 95°C and 80°C heat-induced antigen retrieval for consecutive 2-μm slices from a breast cancer sample (Methods).
(a) Signal-to-noise ratio was calculated based on the ratio of metal ion counts within a rough 2D nuclear segmentation mask to background signal for 2um-thick consecutive slices from the same breast cancer sample (n = 1) that either underwent antigen retrieval at 80 °C for 80 minutes (7 slices) or at 95°C for 30 minutes (5 slices) as part of a one experiment. The first five consecutive images are shown in c) and d). The experiment also included a second independent sample (data not shown). (b) Antibody clones used for antigen retrieval comparison. (c) and (d) Overlays of the pairwise consecutive slices aligned with affine transformation after antigen retrieval at c) 80 °C (images shown for the first 5 slices) and d) 95 °C (images shown for all the slices). Green and magenta indicate two consecutive slices, and white shows overlapping region. Overlapping images were visualized in ImageJ2.