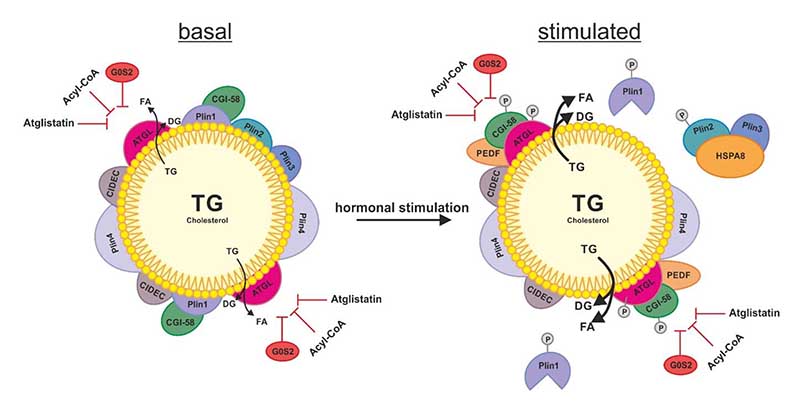
Figure 2.
Schematic overview of the regulation of ATGL on the LD. In basal condition of lipolysis, the LD is decorated with perilipins (Plins) and cell death activator CIDE-3 (CIDEC) to restrict the access of ATGL to the TG stores of the LD. The additional role of Plin1 is to sequester the co-activator protein comparative gene identification 58 (CGI-58) preventing its stimulating interaction with ATGL. ATGL hydrolyzes TG to DG and FA which also takes place to a small extent in basal conditions. Upon hormonal stimulation, the phosphorylation of Plin1, Plin2, CGI-58 and ATGL leads to a change on the surface of the LD: The chaperone heat shock protein HSPA8/hsc70 (HSPA8) shuttles Plin2 and Plin3 to the proteasome for degradation. The dissociation of CGI-58 from Plin1 enables its interaction with ATGL, which activates ATGL’s TG hydrolyzing activity. In both, basal and stimulated state of lipolysis, ATGL can be inhibited by the protein G0/G1 switch gene 2 (G0S2), acyl-CoA and synthetic inhibitor Atglistatin (which is effective in murine ATGL only).