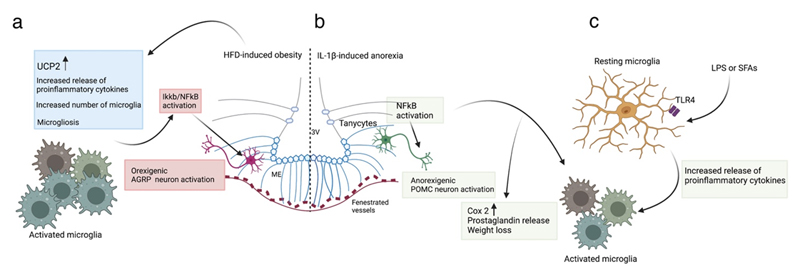
Figure 3. Microglia in HFD-induced obesity and IL-1β/LPS-induced activation.
(a) In HFD-induced obesity, ARH microglia are activated, leading to hypothalamic inflammation with increased release of proinflammatory cytokines, increased expression of microglial UCP2, increased number of microglia and altered microglial morphology (microgliosis)151,155,157. Of note, invalidating IKKB/ NF-KB signalling selectively in AgRP neurons results in an anti-obesity and anti-diabetic phenotype in mice fed a HFD58. (b) Anorexia induced by systemic administration of IL-1β prominently activates NF-KB in tanycytes and microglia. This increases Cox2 expression and prostaglandin release mediating weight loss85. NF-KB activation also directly stimulates POMC transcription in LPS-induced illness146. (c) Microglia of the ARH are sensitive to LPS (used to model sickness-induced anorexia) and saturated fatty acids (SFAs, which stimulate dietary inflammation), activating TLR4 to stimulate the release of proinflammatory cytokines and microglial activation144. ARH, arcuate nucleus of hypothalamus; HFD, high fat diet; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; POMC, pro-opiomelanocortin; SFA, saturated fatty acids; TLR4, toll-like receptor; UCP2, uncoupled protein 2.