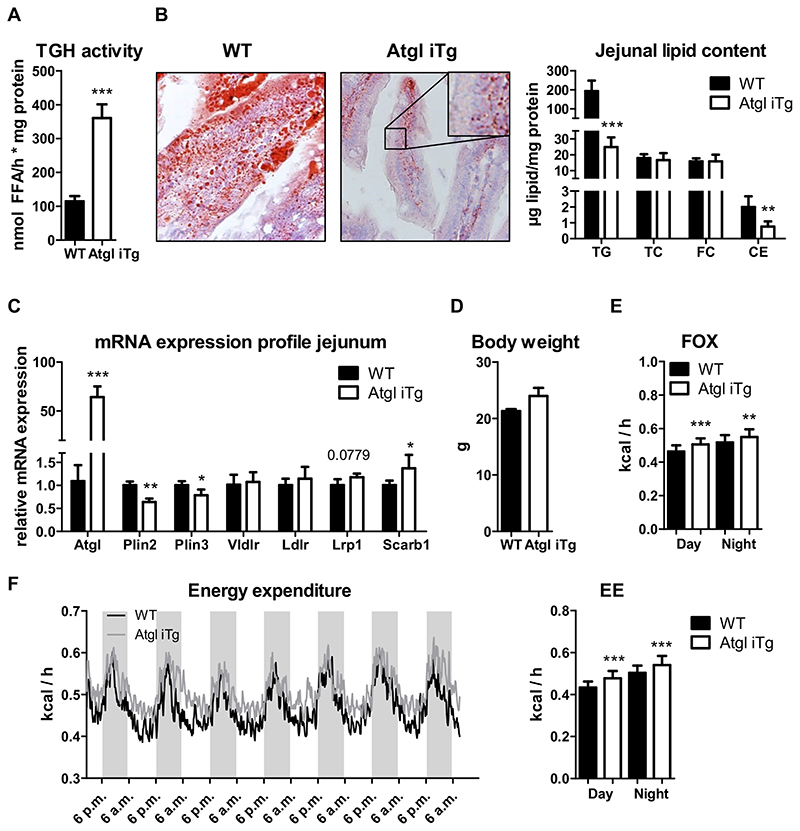
Fig. 6. Increased energy expenditure and fatty acid utilization in HF/HCD-fed Atgl iTg mice.
Jejunal (A) TG hydrolase activity and (B) lipid levels. (C) mRNA expression analysis of Plin2, Plin3, and genes involved in basolateral lipid uptake of HF/HCD-fed mice after 4 h of fasting, normalized to cyclophilin A. (D—F) After 10 weeks of HF/HCD feeding, mice were housed in metabolic cages, and fatty acid oxidation (FOX) and energy expenditure (EE) were analyzed. Data represent mean values of 16—18 week-old female mice (n = 3—5) ± SD. * p < 0.05; ** p ≤ 0.001; *** p ≤ 0.001.