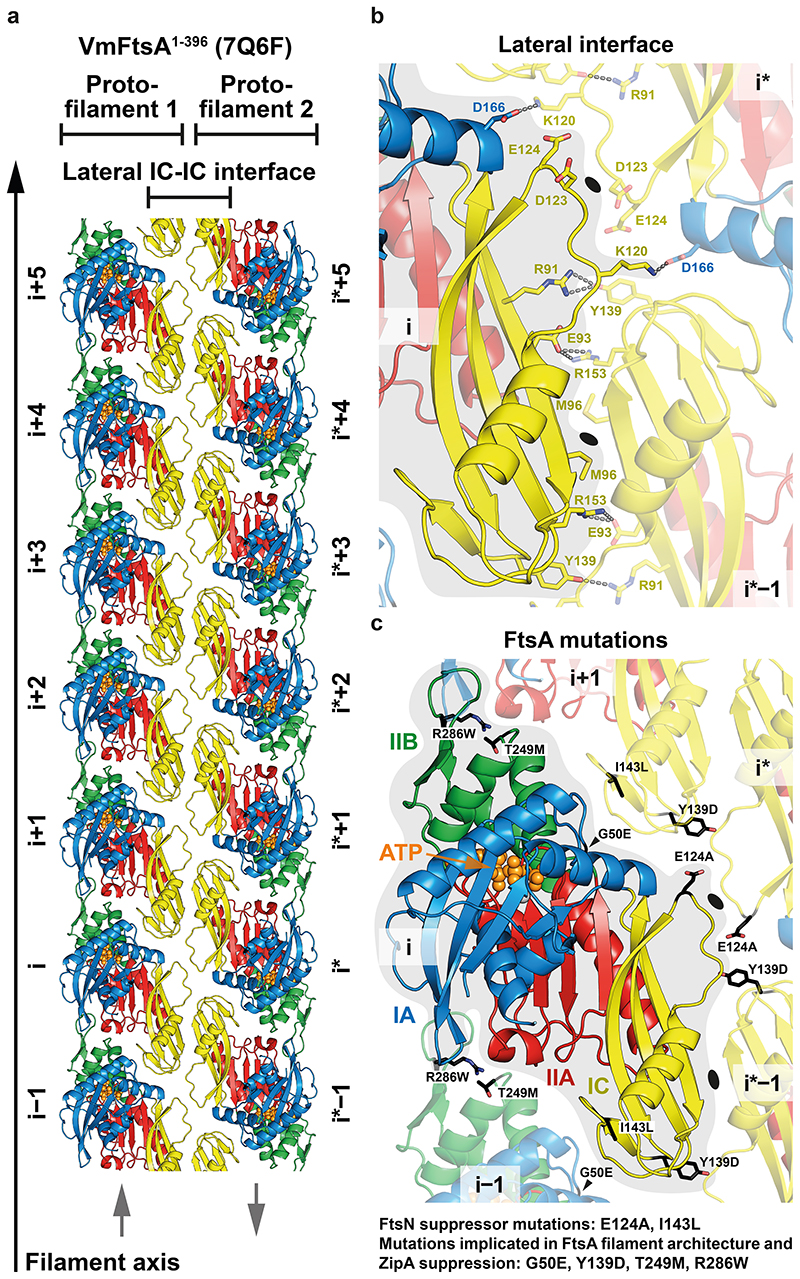
Figure 1. VmFtsA crystallises as an antiparallel double filament via IC domains.
a, Top view of the VmFtsA1-396 antiparallel double filament in cartoon representation from the membrane-proximal side (PDB 7Q6F). The lateral interface is almost exclusively formed by the IC domain (yellow). Grey arrows indicate the relative orientations of FtsA monomers in each protofilament. b, Side chain interactions in the lateral filament interface. Each FtsAi contacts two neighbouring FtsAs, FtsAi*-1 and FtsAi*, in the opposing protofilament. Both interfaces have local C2 symmetry (black ellipses). c, Reported FtsN suppressor mutations in E. coli FtsA, E124A27 and I143L16, and ZipA suppressor mutations that recently have been implicated in FtsA (double) filament formation32 are mapped on the VmFtsA double filament structure. All mutations are part of filament interfaces. For further information about the suppressor mutants see Supplementary Table T2.