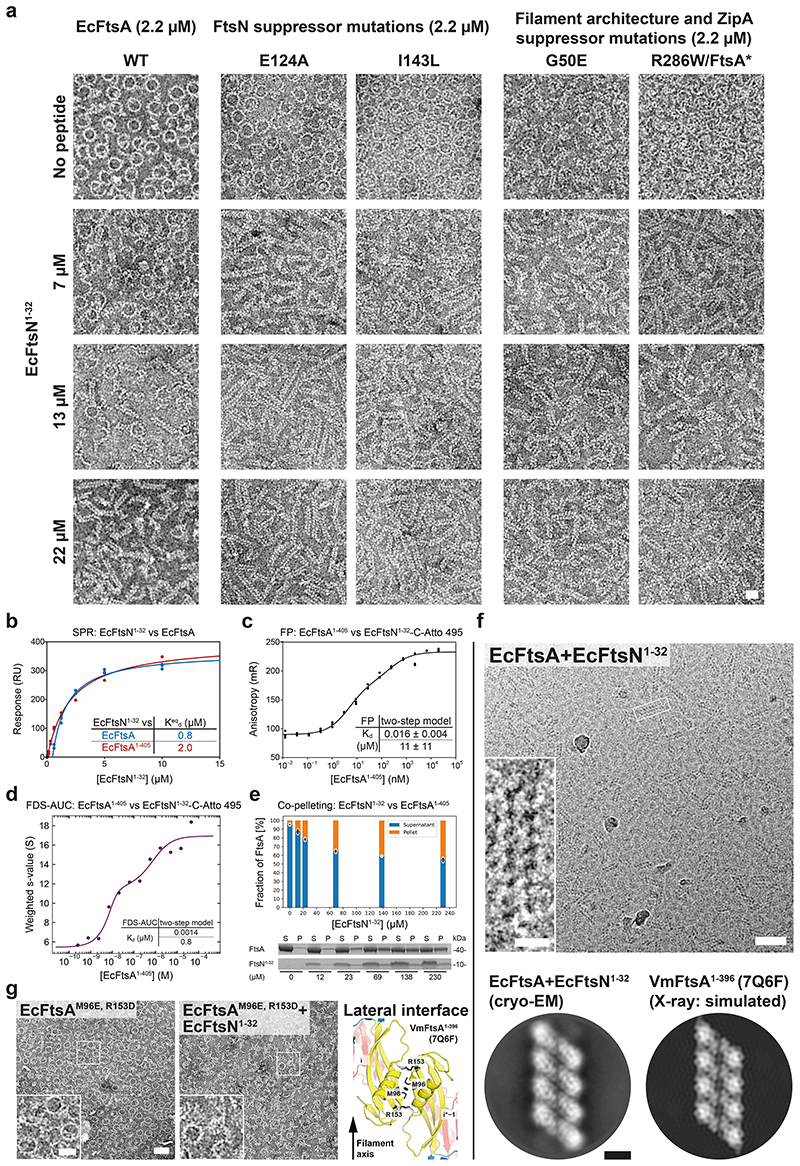
Figure 2. EcFtsA forms antiparallel double filaments upon binding EcFtsN1-32.
a, Negative stain electron micrographs of EcFtsA mutants on supported lipid monolayers with increasing concentrations of EcFtsN1-32. EcFtsA forms “mini-rings” in the absence of FtsN peptide, as described previously37. With increasing EcFtsN1-32 concentrations, EcFtsA forms fewer “mini-rings” and more double filaments. Introduction of the G50E, E124A, I143L or R286W mutations into EcFtsA facilitates filament formation at lower concentrations of EcFtsN1-32. See also Figure 1c and Supplementary Table T2. At least two independent grids were examined per condition. Scale bar, 20 nm. b, SPR equilibrium response titration of EcFtsN1-32 binding to immobilised EcFtsA (blue) or EcFtsA1-405 (red). EcFtsN1-32 has micromolar affinity for both FtsA proteins. c, EcFtsA1-405 titration into EcFtsN1-32-C-Atto 495. Data were fitted with a two-step model, with transitions being indicative of FtsN binding and polymerisation (panel d). A representative triplicate is shown. Kds are given as mean ± SEM from five independent experiments. d, Weight-averaged sedimentation coefficients of a EcFtsA1-405 titration into fluorescently labelled EcFtsN1-32-C-Atto 495 by FDS-AUC shows that EcFtsN1-32 is part of higher order FtsA polymers. Data were fitted to a two-step model, recapitulating the FP data in panel c. e, Co-pelleting assay of EcFtsN1-32 titrated into EcFtsA1-405 indicates that EcFtsN1-32 induces FtsA polymerisation. A representative SDS-PAGE gel is shown. Given are mean ± sd (black lines) of technical duplicates (white dots). P: pellet, S: supernatant. f, EcFtsA and EcFtsN1-32 form double filaments on lipid monolayers as determined by cryo-EM. 2D classification confirmed the antiparallel arrangement of the observed double filaments. A computed 2D projection from the VmFtsA double filament crystal structure (PDB 7Q6F) is shown for comparison. Two independent grids were examined. Data was collected on one grid. Scale bars, 50 nm, 10 nm (inset), 5 nm (2D class averages). g, The lateral interface mutant EcFtsAM96E, R153D is deficient in FtsN1-32-dependent double filament formation as determined by negative stain electron microscopy on a supported lipid monolayer. Two independent grids were examined per condition. Scale bar, 50 nm, 20 nm (inset).