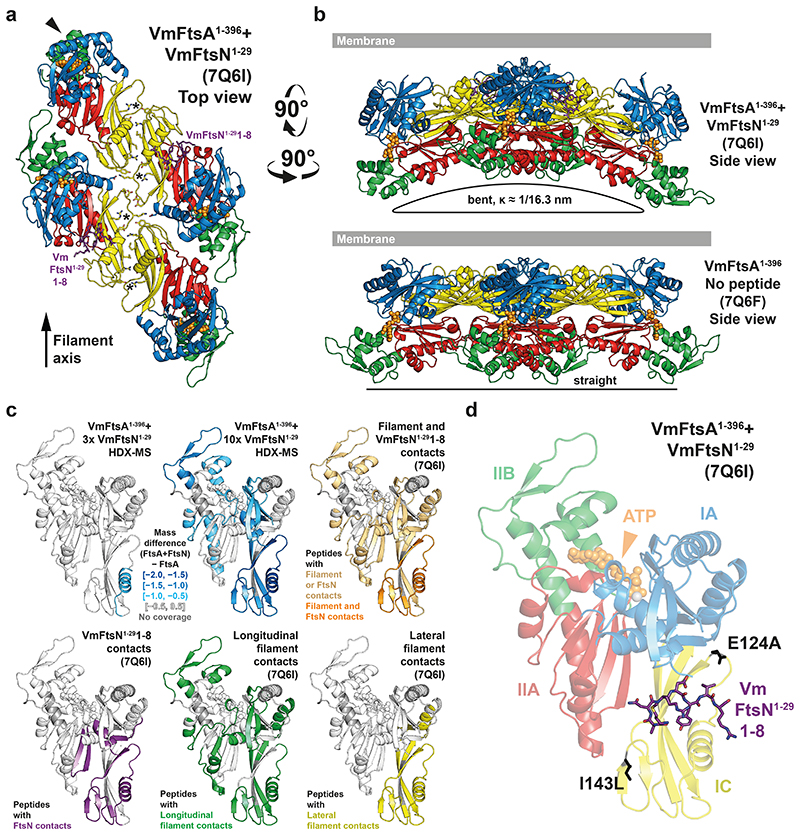
Figure 3. VmFtsA1-396 and VmFtsN1-29 crystallise as short, bent double filaments.
a, 16 FtsA monomers in the ASU of the co-crystal structure are organised into short, antiparallel, and curved tetramers (see also Supplementary Movie M1). Top view of a representative tetramer (which requires crystal symmetry to be applied to the PDB coordinates) from the membrane-proximal side. Residues 1-8 of VmFtsN1-29 (purple sticks) are present in the closed subunit of each protofilament. IC domains are tilted against each other compared to the VmFtsA1-396 double filament structure (PDB 7Q6F), presumably destabilising the R91-Y139 interaction (asterisks) in the lateral interface. The IIB domain of the top left monomer (chain D) is partially disordered (arrowhead). b, A comparison of the side views of the PDB 7Q6I and PDB 7Q6F crystal structures illustrates that the 7Q6I tetramer is bent along the filament axis. c, HDX-MS analysis of VmFtsA1-396 with three- (30 μM) or ten-fold molar excess (100 μM) of VmFtsN1-29, confirming VmFtsN1-29 to bind in the IA-IC interdomain cleft of FtsA. Peptides that are protected in the presence of VmFtsN1-29 (slower exchange of hydrogen for deuterium) are highlighted in blue. Presumably because high concentrations of VmFtsN1-29 induce polymerisation of VmFtsA1-396 (Extended Data Figure 2d, e), peptides mapping to the filament interfaces are protected as well. For orientation, peptides are coloured according to their involvement in different interfaces of the VmFtsA1-396-VmFtsN1-29 co-polymer (PDB 7Q6I). d, Residues 1-8 of VmFtsN1-29 bind in the IA-IC interdomain cleft of VmFtsA1-396. Positions of FtsN suppressor mutations E124A27 and I143L16 are shown in black.