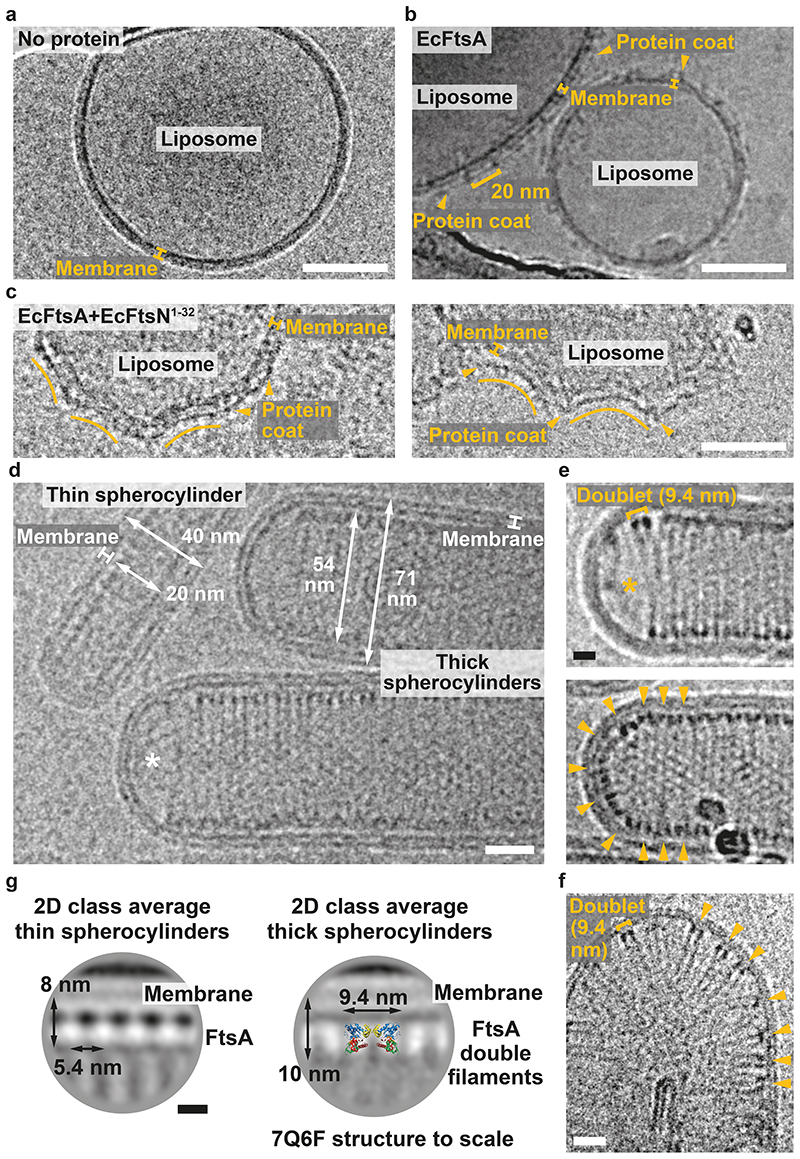
Figure 4. EcFtsA-FtsN1-32 double filaments orient inside liposomes.
a, Cryo-EM micrograph showing a spherical liposome with no proteins added. The carbon edge of the grid is visible at the top of the image. Scale bar, 50 nm. b, Cryo-EM micrograph of liposomes with EcFtsA (arrowheads) bound to the outside. Liposomes show no indentations. The protein coat shows a 20 nm repeat, indicating the presence of EcFtsA “mini-rings” (see also Extended Data Figure 3b). The carbon edge of the grid is visible at the bottom left of the image. Scale bar, 50 nm. c, Cryo-EM micrographs of liposomes with EcFtsA-FtsN1-32 filaments (arrowheads) bound to the outside. Liposomes show indentations. See Salje et al. for a comparison with MreB filaments added to liposomes4. Scale bar, 50 nm. d, Co-encapsulation of EcFtsA and EcFtsN1-32 in liposomes produces thin and thick protein-filled spherocylinders (rods) with diameters of ~40 nm and ~70 nm, respectively. EcFtsA-FtsN1-32 filaments align with the short axis of the spherocylinders. There are no filaments in the hemisphere of a thick spherocylinder (asterisk). See Hussain et al. for a comparison with MreB filaments encapsulated into liposomes34. Scale bar, 20 nm. e, Cryo-EM micrographs of EcFtsA-FtsN1-32 double filaments in thick spherocylinders. Top: EcFtsA-FtsN1-32 double filaments align with the short axis of thick spherocylinders. There are no filaments in the hemisphere of the spherocylinder (asterisk). Bottom: EcFtsA-FtsN1-32 double filaments align with the short axis in the cylindrical part of the spherocylinder but are randomly oriented in the hemisphere (arrowheads). Scale bar, 10 nm. f, Liposome with few EcFtsA-FtsN1-32 double filaments inside. EcFtsA-FtsN1-32 double filaments are randomly oriented in the semi-circular part of the liposome but are more aligned in the cylindrical part (arrowheads). Scale bar, 20 nm. For panels a-f, at least two independently prepared grids were examined per condition. g, 2D class averages of FtsA membrane attachment sites in thin and thick spherocylinders. EcFtsA-FtsN1-32 are organised into single protofilaments in thin spherocylinders. Thick spherocylinders contain EcFtsA-FtsN1-32 double filaments. End view of the VmFtsA1-396 double filament structure (PDB 7Q6F) shown to scale. Scale bar, 5 nm.