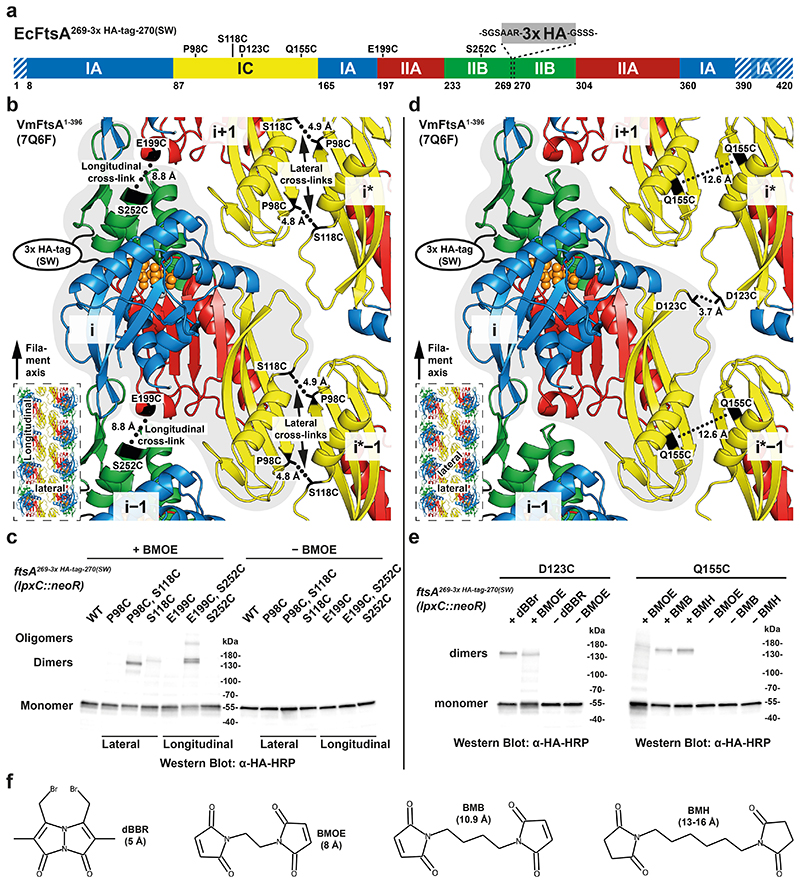
Figure 5. FtsA forms antiparallel double filaments in vivo.
a, Domain architecture of EcFtsA (amino acids positions are the same for VmFtsA). Positions of cysteine mutations and the 3x HA-tag (comprising 40 amino acids including linkers, grey) are indicated. Striped areas correspond to disordered residues in the VmFtsA1-396 double filament structure (PDB 7Q6F). b, Cysteine mutation pairs FtsA3x HA, P98C, S118C and FtsA3x HA, E199C, S252C probing the lateral and longitudinal filament interfaces, respectively, are highlighted on the VmFtsA double filament structure (PDB 7Q6F). Cβ-Cβ distances between cysteines and the position of the 3x HA-tag are indicated. The inset highlights the probed interfaces in the context of the double filament. SW: sandwich fusion. c, Western blot of cell lysate from FtsA cysteine mutant E. coli strains after in vivo cysteine cross-linking (+ BMOE) or without cross-linking (− BMOE). Signal for covalent FtsA dimers can be detected for both double cysteine mutants. For ftsA3x HA, E199C, S252C, higher order oligomers can be detected because of the open symmetry of the longitudinal contact, which leads to chaining. Similar results were achieved in biological triplicate. d, Cysteine mutations ftsA3x HA, D123C and ftsA3x HA, Q155C probing the lateral FtsAi-FtsAi* and FtsAi-FtsAi*−1 filament interfaces, respectively, are highlighted on the VmFtsA double filament structure (PDB 7Q6F). Cβ-Cβ distances between cysteines and the position of the 3x HA-tag are indicated. Both single cysteine mutations utilise the local C2 symmetry of the respective lateral interface for cross-linking. The inset highlights the probed interfaces in the context of the double filament. e, Western blot of cell lysate from FtsA cysteine mutant E. coli strains after in vivo cysteine cross-linking with thiol-directed cross-linkers of different lengths (“+ cross-linker”) or without cross-linking (“− cross-linker”). Signal for a FtsA dimer can be detected after using dBBr and, to a lesser extent, BMOE cross-linking in the ftsA3x HA, D123C mutant. For the ftsA3x HA, Q155C mutation, FtsA dimers can be detected after cross-linking with BMB or BMH, but not with BMOE. Similar results were achieved in biological duplicate. f, Structures and estimated cross-linking distances for cross-linkers used in this study. dBBr: dibromobimane, BMOE: bismaleimidoethane, BMB: 1,4-bismaleimidobutane, BMH: bismaleimidohexane.