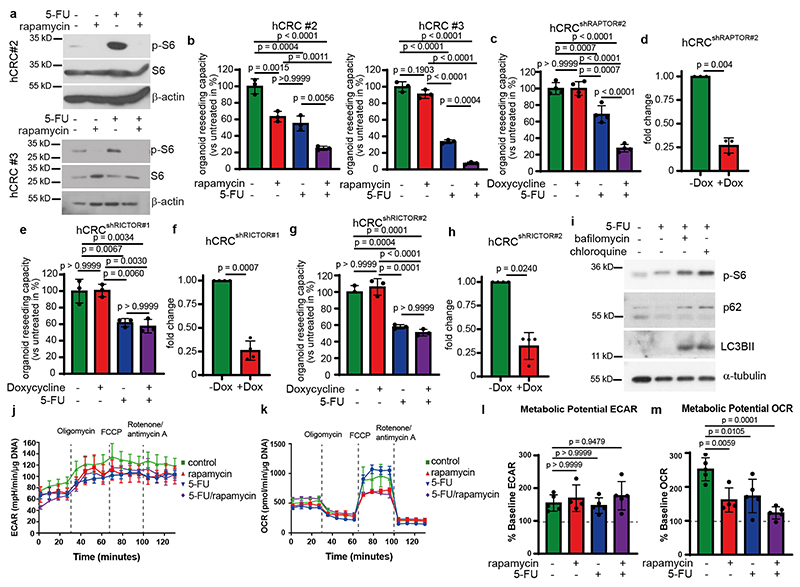
Extended Data Fig. 1. (Related to Figure 1): CRC resistance to 5-FU depends on mTORC1 but not mTORC2.
a, Immunoblot analysis of two different human tumor organoid lines derived from sporadic CRC treated as indicated (n=3).
b, Reseeding capacity of hCRC organoid lines treated with 5-FU, rapamycin or 5-FU/rapamycin (n=3, one of three biological replicates).
c, Reseeding capacity of doxycycline-inducible hCRCshRAPTORr#2 tumor organoids treated as indicated (n=4, one of three biological replicates).
d, Raptor qRT-PCR analysis of doxycycline treated hCRCshRAPTOR#2 tumor organoids (n=3 biological replicates).
e, Reseeding capacity of doxycycline-inducible hCRCshRICTOR tumor organoids treated as indicated (n=4, one of three biological replicates).
f, Rictor qRT-PCR analysis of doxycycline treated hCRCshRictor#1 tumor organoids (n=3 biological replicates).
g, Reseeding capacity of doxycycline inducible hCRCshRICTOR#2 tumor organoids treated as indicated (n=4, one of three biological replicates).
h, Rictor qRT-PCR analysis of doxycycline treated hCRCshRictor#2 tumor organoids (n=3 biological replicates).
i, Immunoblot analysis of Lgr5 - tumor organoids treated as indicated (n=3).
j) Profiles for Extracellular Acidification Rate (ECAR) of AOM/DSSATKN tumor organoids treated as indicated for 24h (n=4 for rapamycin treated organoids in all other conditions n=5 biological replicates of one experiment).
k) Profiles for Oxygen Consumption Rate (OCR) of AOM/DSSATKN tumor organoids described in (j) (n=4 for rapamycin treated organoids in all other conditions n=5 biological replicates of one experiment).
l) Percentage of metabolic potential over baseline in ECAR in organoids described in (j) (n=4 for rapamycin treated organoids in all other conditions n=5 biological replicates of one experiment).
m) Percentage of metabolic potential over baseline in OCR in organoids treated described in (j) (n=4 for rapamycin treated organoids in all other conditions n=5 biological replicates of one experiment).
All data are mean ±SD (except for j, k where data are mean ±SEM) and analysed by twotailed Student’s t-test (d, f, h) or 1-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparison (b, c, e, g, l, m).