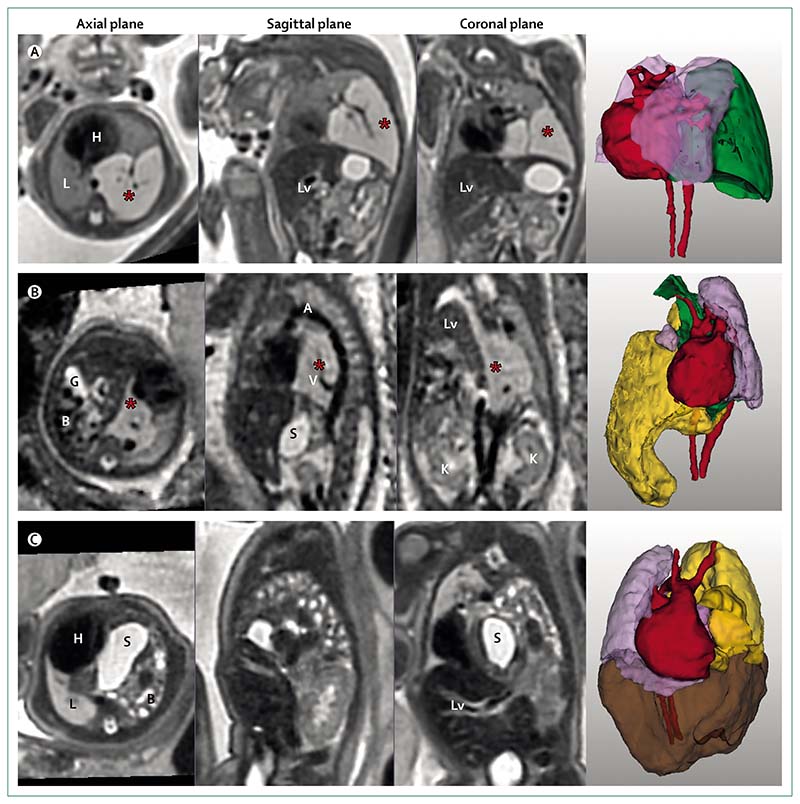
Figure 2. T2-weighted MRI and three-dimensional models of three fetuses with lesions of the thorax.
(A) Fetus of 24 weeks’ gestation with a lesion of left lower lung showing a microcystic congenital pulmonary airway malformation of the left lower lobe (marked by an asterisk), also shown in 3D (green), with heart (red) and lungs (lilac). (B) Fetus of 24 weeks’ gestation with bronchopulmonary sequestration (marked by an asterisk) and right congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Reorientation to true sagittal shows a feeding vessel arising from the aorta. Note the right-sided diaphragmatic hernia containing the bowel (yellow), gallbladder, and stomach. Kidneys are shown in the coronal plane. 3D models show bronchopulmonary sequestration (green), lungs (lilac), and heart (red). (C) Fetus of 33 weeks’ gestation with a left-sided congenital diaphragmatic hernia, containing stomach and intestine (yellow), and liver (brown) within the hernia, and showing the heart (red) and lung (lilac) in relation to hernial content. 3D=three-dimensional. A=aorta. B=bowel. G=gallbladder. H=heart. K=kidney. L=lung. Lv=Liver. S=stomach. V=vessel.