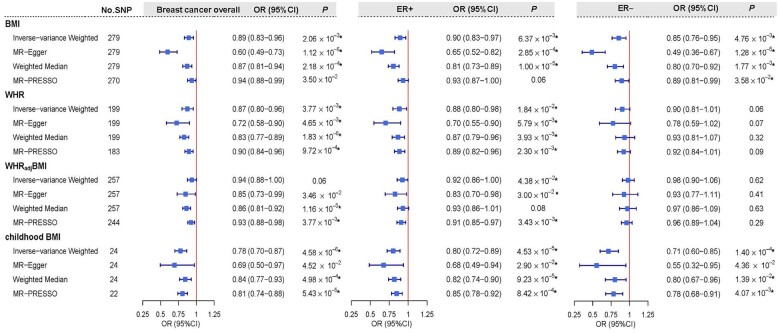
Figure 2.
Estimated total effects of obesity-related traits on the risk of breast cancer using univariable Mendelian randomization
Boxes denote the point estimates of causal effects, and error bars denote 95% confidence intervals. Asterisks (*) denote the tests survived false discovery rate (FDR) correction (PFDR < 0.05). Inverse-variance weighted approach was used as primary analysis; MR–Egger, weighted-median and MR-PRESSO were used as sensitivity analyses.
BMI, body mass index; WHR, waist-to-hip ratio; WHRadjBMI, waist-to-hip ratio adjusted for body mass index; ER, oestrogen receptor; No. SNP, number of instrumental variables; OR, odds ratio.