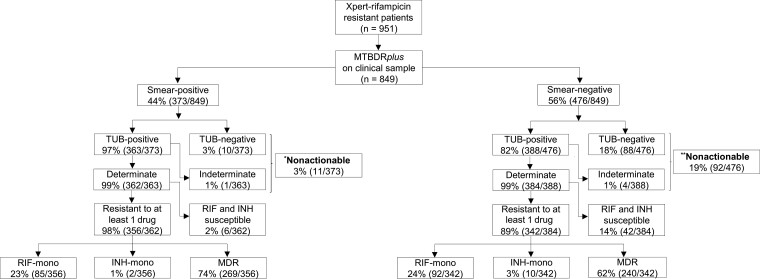
Figure 2.
Direct MTBDRplus testing of sputum is successful in almost all smear-positives and most smear-negatives; however, it fails to generate a susceptibility result in a significant minority of smear-negatives (1 in 5), indicating that a failure to detect tuberculosis is the primary cause of drug resistance being missed (ie, nonactionable results). Furthermore, a significant minority of Xpert RIF-resistant patients do not have MDR per MTBDRplus, suggesting a continued role for isoniazid drug susceptibility testing. Importantly, in patients with actionable MTBDRplus results, sensitivity and specificity for resistance did not differ by smear status. Resistance classifications on the bottom 2 rows of boxes are per direct MTBDRplus. Of the 951 Xpert rifampicin-resistant patients, only 849 were confirmed culture-positive. *Indirect smear-positive MTBDRplus results: MDR (n = 7), RIF-mono (n = 0), INH-mono (n = 1), fully susceptible (n = 3), and nonactionable (n = 0). **Indirect smear-negative MTBDRplus results: MDR (n = 69), RIF-mono (n = 0), INH-mono (n = 3), fully susceptible (n = 20), and nonactionable (n = 0). Abbreviations: INH, isoniazid; mono, monoresistant; MDR, multidrug-resistant; RIF, rifampicin; TUB, TUB-band; Xpert, Xpert MTB/RIF.