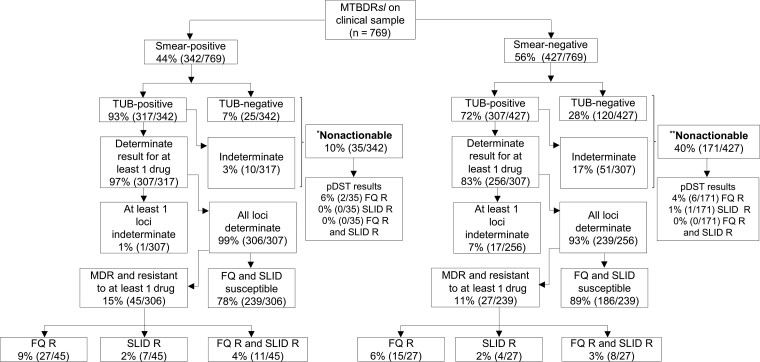
Figure 3.
Although direct MTBDRsl testing of sputum is successful in most patients, it results in relatively high proportions of nonactionable results in smear-positives and especially in smear-negatives. MTBDRsl failed in 4 of 10 smear-negative patients with Xpert-diagnosed rifampicin resistance. As seen for MTBDRplus, a failure to generate an actionable result on smear-negatives was the primarily cause of missed resistance (as opposed to a false-negative susceptible result). Resistance classifications on the bottom 2 rows of boxes are per direct MTBDRsl. Of the 849 culture-positive patients, only 769 had usable pDST (80-contaminated). *Indirect smear-positive MTBDRsl results: FQ-R (n = 3), SLID-R (n = 0), FQ-R and SLID-R (n = 0), fully susceptible (n = 33), and nonactionable (n = 0). **Indirect smear-negative MTBDRsl results: FQ-R (n = 7), SLID-R (n = 4), FQ-R and SLID-R (n = 2), fully susceptible (n = 175), and nonactionable (n = 0). Abbreviations: FQ, fluoroquinolones; MDR, multidrug-resistant; pDST, phenotypic drug susceptibility testing; R, resistant; SLID, second-line injectable drug; TUB, TUB-band.