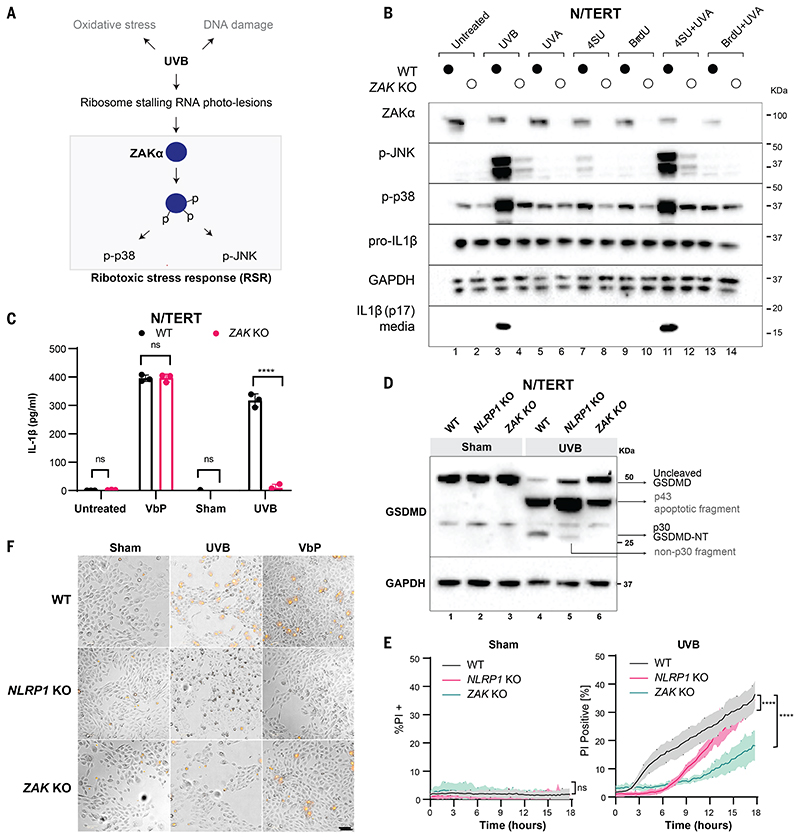
Figure 1. ZAKα is required for UVB-triggered NLRP1 inflammasome activation.
(A) Schematic indicating types of cellular damage caused by UVB irradiation. UVB activates ribotoxic stress response (RSR) signaling through ZAKα. (B) Immunoblot of WT N/TERT cells or ZAK KO (sg4) N/TERT cells treated with the indicated combinations of photosensitizer (10 μM) for 4 hours with or without UVA. UVB (100 mJ/cm2) was used as a positive control. *, residual signal after membrane stripping. (C) IL-1β ELISA of WT or ZAK KO (sg4) N/TERT cells after VbP (3 μM) treatment, sham or UVB (100 mJ/cm2) irradiation. Cell culture media were collected 24 hours later. (D) GSDMD immunoblot of WT, NLRP1 KO, ZAK KO (sg4) N/TERT cells treated with UVB (100 mJ/cm2) or sham-irradiated. Cell lysates were harvested 24 hours later. Different GSDMD cleavage fragments are shown by black arrows. Note that the GSDMD antibody used in this experiment recognizes all GSDMD-cleaved products. In NLRP1 KO cells UVB leads to a weak band <30 kDa. (E) Quantification of the percentage of PI-positive WT, NLRP1 KO, ZAK KO (sg4) N/TERT cells after sham or UVB (100 mJ/cm2) irradiation. (F) Representative images of PI inclusion 5 hours post irradiation from 3 independent experiments. Scale bar represents 100 μm. Error bars represent standard errors of the mean (S.E.M.) from three biological replicates, where one replicate refers to an independent seeding and treatment of the cells. The significance values were calculated based on two-way ANOVA followed by Sidak’s test for multiple pairwise comparisons in (C), and two-tailed Kolmogorov-Smirnov test at 95% confidence interval in (E). ns, non-significant, ****P<0.0001.