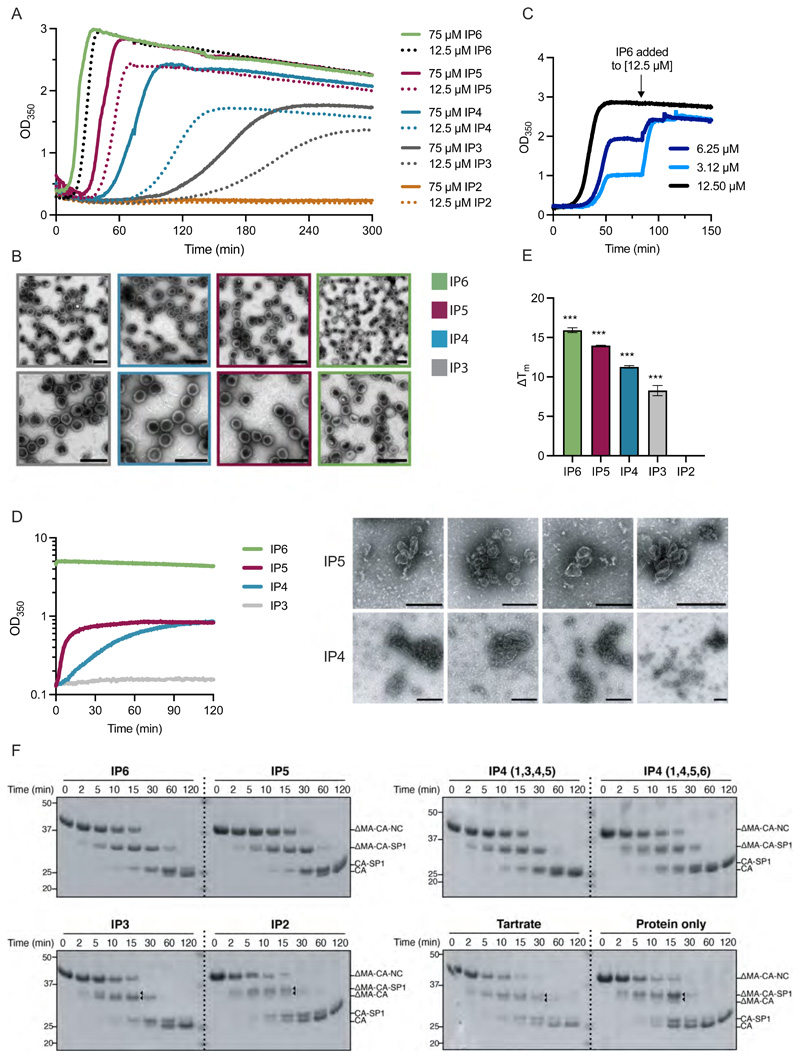
Figure 3. Immature particles assemble more slowly with smaller IPs, are less stable and have altered Gag processing relative to particles assembled in the presence of IP5 or IP6.
(A) In vitro assembly of immature particles using recombinant DMA-CANC protein. 7.5 μM RNA was added to 75 μM DMA-CANC and assembly monitored through light scattering changes at 350 nm at 37 °C. Indicated IPs were added at equimolar DMA-CANC concentration or 12.5 μM, to achieve a stoichiometry with immature hexamers of 6:1 or 1:1, respectively. Representative of two experiments. (B) EM images of negative-stained samples of the final assembly reactions shown in (A). Scale bars are 200 nm. (C) In vitro assembly reaction of immature particles as in (A) except IP6 was added at stoichiometric ratios with respect to immature hexamers of 1:1 (12.5 μM), 0.5:1 (6.25 μM) or 0.25:1 (3.12 μM). Once assembly had plateaued, additional IP6 was added to achieve 1:1 stoichiometry, resulting in similar final yields by light scattering. Representative of two experiments. (D) In vitro assembly of mature particles using 150μM recombinant CA protein and 2.5 mM of the indicated IP. EM images of negative-stained samples of the final assembly reactions are shown to the right. Size bars are 200 nm. Representative of at least three experiments. (E) Thermostability of in vitro assembled particles with 7.5 μM RNA, 75 μM ΔMA-CANC and 12.5 μM IP was measured by differential scanning fluorimetry (DSF). The change in melt temperature (ΔTm) was calculated with respect to the thermostability of unassembled ΔMA-CANC protein. An unpaired t test against unassembled ΔMA-CANC was used for statistical analysis and significant differences indicated (P < 0.0005 (***)). (F) In vitro assembled particles as in (E) but with an additional condition including 375 μM Tartrate rather than IP and unassembled DMA-CANC were incubated with recombinant HIV-1 protease for the indicated times and analysed by SDS PAGE and western blot. The probable cleavage products, based on size, are indicated. Triangles point to additional cleavage products that are not present in particles assembled with IP6.