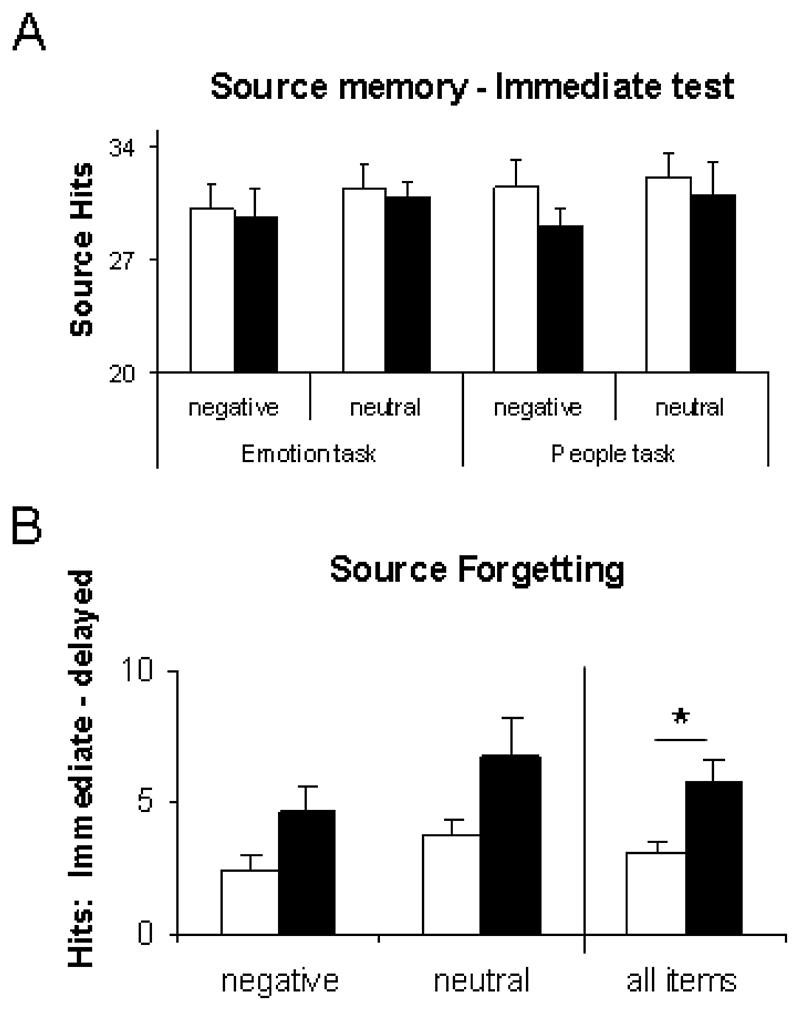
Figure 2. Behavioural performance on the source memory task.
(A) The number of correctly attributed sources at the immediate test did not differ between groups (Sleep/Wake), encoding valences (negative/neutral), or tasks (EMOTION/PEOPLE). (B) Source forgetting, calculated as correct immediate source attributions minus correct delayed source attributions, differed between groups. Participants who slept during the retention interval correctly attributed more sources (main effect of retention type P=0.03). Furthermore, negative sources were more frequently remembered than neutral sources (main effect of valence P=0.02). Error bars show 1 SEM.