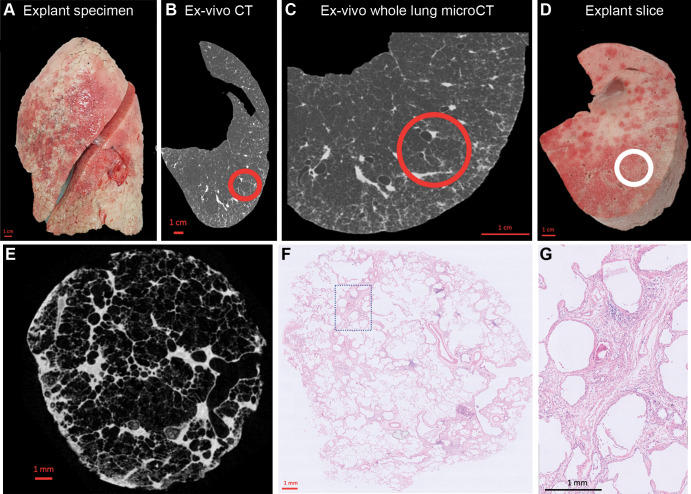
Figure 1:
Study design. (A) Photograph shows the explanted lung frozen solid in liquid nitrogen fumes. (B) Axial noncontrast ex vivo CT scan of the specimen is obtained while it is frozen. (C) Whole-lung micro-CT scan is obtained for better spatial resolution. (D) Photograph shows the lung sliced transversally in 2-cm slices. (E) Micro-CT scan of a core sample (indicated with the circle in B–D) is obtained. (F) Matched histologic image (hematoxylin-eosin stain; magnification, ×5) is shown at the same location as the micro-CT scan. (G) High-magnification histologic image (hematoxylin-eosin stain; magnification, ×20) shows paraseptal fibrosis.