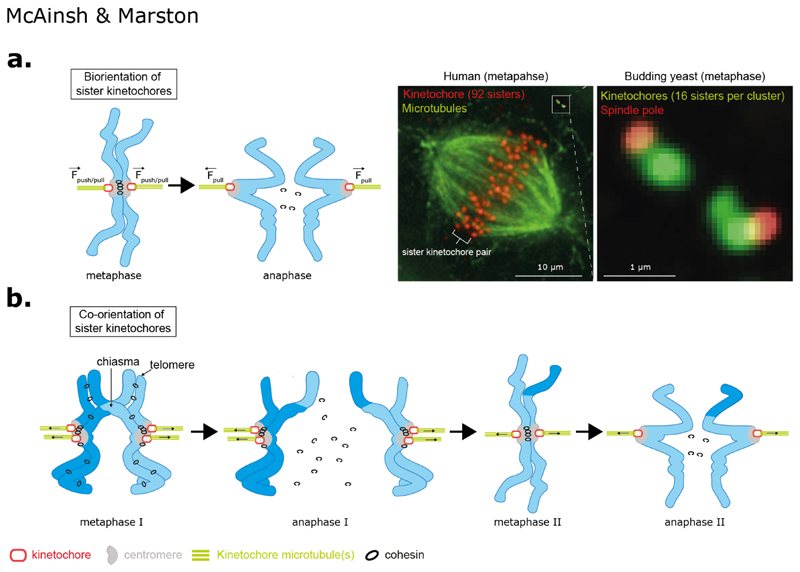
Figure 1. Geometries of chromosome segregation during mitosis and meiosis.
(a) Top left: In mitosis the replicated chromosomes (sister chromatids - blue) are bioriented with sister kinetochores (red) in a back-to-back geometry and embedded in pericentromeric chromatin domain (grey). Sister chromatids are physically held together by cohesin molecules which trap the two DNA stands (black circles). The plus-end of spindle microtubules (green; either singular in budding yeast or multiple in animal cells) are embedded in the kinetochore with their minus-ends projecting towards the centrosomes (human) or spindle pole bodies (budding yeast). Pulling forces generated by kinetochore microtubule attachments pull sister chromatids apart in anaphase once cohesin is cleaved (on satisfaction of the spindle assembly checkpoint). Top Right: Mitotic spindle in a human cell (kinetochores red and microtubules (green) compared to budding yeast (kinetochores green and spindle pole bodies in red). In yeast the 32 sister kinetochores form two clusters along the spindle axis, which is ~1 μm in length. This is similar to distance between two sister kinetochores in humans. In humans the sister kinetochores are aligned along the spindle axis.
(b) In meiosis I, replicated maternal and paternal (homologous) chromosomes are physically connected are a result of crossover recombination, which generates chiasmata, together with sister chromatid cohesion distal to the chiasmata. Sister kinetochores are attached to microtubules from the same pole and are said to be co-oriented. An anaphase I, cohesin is cleaved only on chromosomes arms (pericentromeric cohesin is protected from cleavage by shugoshin-PP2A; reviewed in (158)) which resolves chiasma and allows homologous chromosomes to segregate to opposite poles. In meiosis II, sister kinetochores biorient and the pericentromeric cohesin resists the pulling forces from microtubules. During anaphase II, pericentromeric cohesin is cleaved and sister kinetochores segregate to opposite poles.