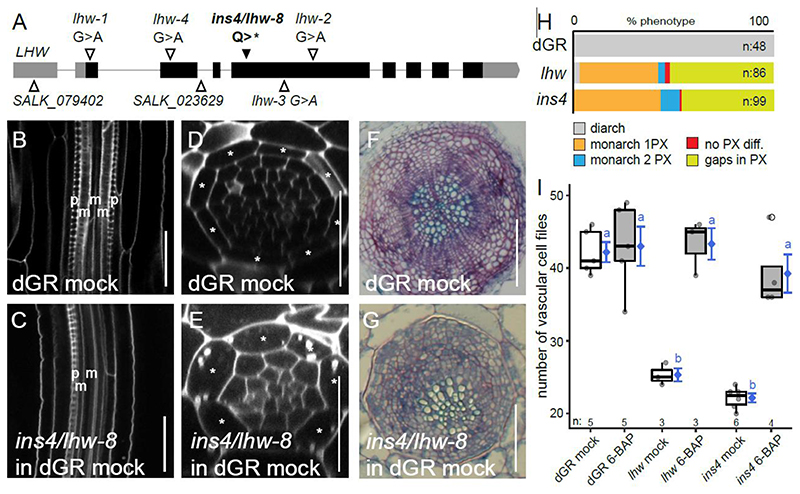
Figure 3. The insensitive mutant ins4 is a novel lhw allele.
(A) Alleles of lhw mutants with ins4/lhw-8 having a point mutation, resulting in a premature stop codon in exon (black bar) 4 of LHW. (B-C) Longitudinal view of the root vascular tissue shown for dGR (B) and ins4/lhw-8 (dGR) (C). (D-E) Optical cross-section through the root meristem of dGR (D) and ins4/lhw-8 (dGR) (E) show smaller vascular cylinder for ins4/lhw-8 (dGR). (F-G) Secondary growth phenotype can be observed in sections of dGR (F) and ins4/lhw-8 (dGR) (G) through the hypocotyl of 3-week-old seedlings. Scale bars in B-E are 25 μm and in F-G 100 μm. (H) The frequency of xylem differentiation (diff.) phenotype plotted for dGR, lhw and ins4 (dGR). The asterisks mark the endodermis cells in D-E, ‘p’ an ‘m’ represent protoxylem and metaxylem cell files in B-C. (I) The number of vascular cell files of 1-week-old seedlings treated with cytokinin (6-BAP). Black lines indicate mean values and grey/white boxes indicate data ranges. n marks the number of datapoints for each sample. The mean and its precision are plotted as the blue rhombus with blue SE bars. Count data samples were compared pairwise based estimated means of a generalized linear model with log link function. Common blue lower-case letters (compact letter display) at these means indicate non-significantly different groups as determined by the pairwise comparisons (Table S1).