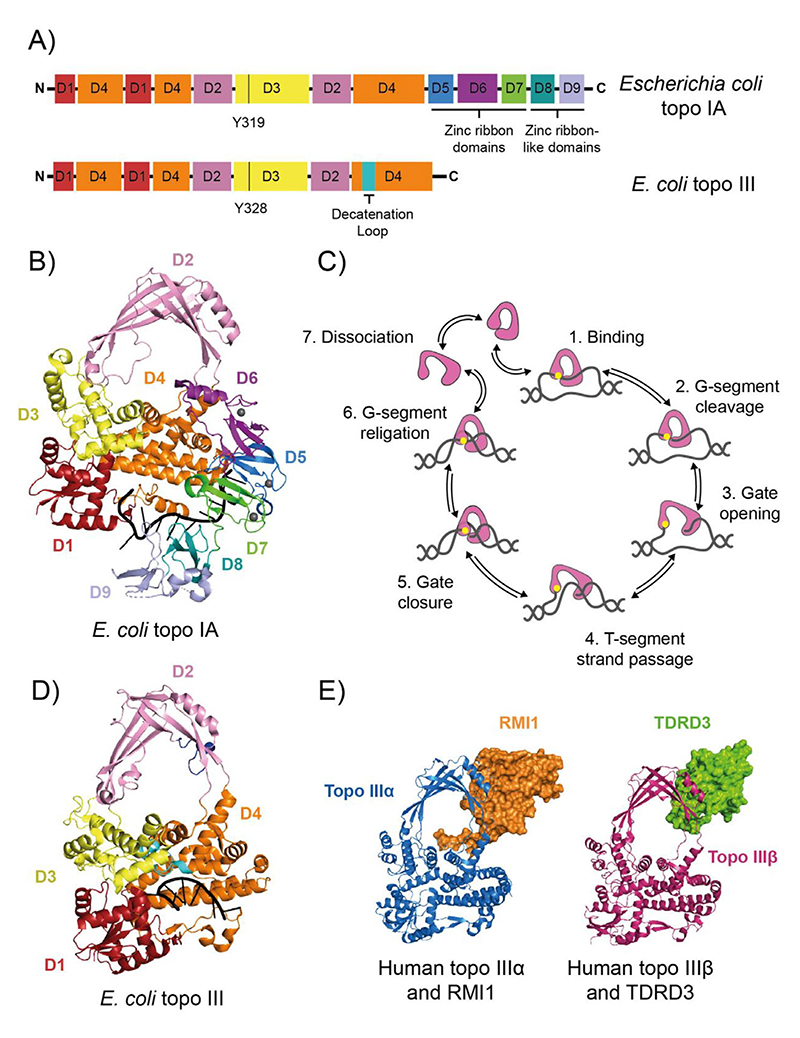
Figure 2. Type IA DNA topoisomerases.
(A) Protein domain organisation of Escherichia coli DNA topoisomerase IA (topo IA) and DNA topoisomerase III (topo III). Black vertical lines represent the active site tyrosines. (B) Crystal structure of E. coli topo I bound to ssDNA (PDB: 4RUL).[20] (C) Strand-passage mechanism for type IA topos. (1) topo binds G-segment ssDNA region, (2) the G-segment is cleaved. (3) The topo DNA-gate is opened, (4) which allows T-segment transfer through the cleaved G-strand. (5) The DNA gate is closed, (6) and the G-strand is re-ligated, changing the linking number by 1. (7) The topo can then go through another round of relaxation or dissociate from the DNA. Type IA topo (domains 1–4) is in pink, the active site tyrosine is yellow and the DNA is grey. (D) Crystal structure of E. coli topo III bound to ssDNA (PDB: 2O54).[26] (E) Crystal structures of human topo IIIα (blue) bound to RMI1(orange) (PDB: 4CGY),[39] and human topo IIIβ (magenta) bound to TDRD3 (green) (PDB: 5GVE).[60] For panels A, B and C, the topo I and III domains are colour coded as follows: D1 is red, D2 is pink, D3 is yellow, D4 is orange, D5 is marine blue, D6 is purple, D7 is green, D8 is teal, and D9 is light blue