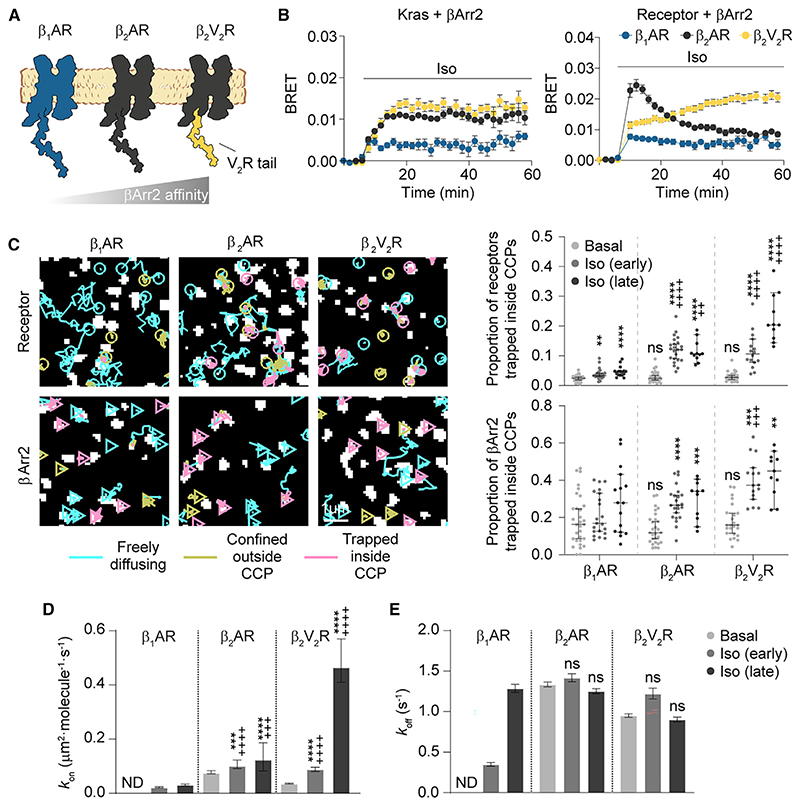
Figure 2. Affinity for receptor C-tail governs βArr2 interaction with receptors and plasma membrane behavior.
(A) Schematic of the investigated receptors.
(B) Kinetics of βArr2 recruitment to the plasma membrane (Kras) and receptor upon isoproterenol (10 μM) stimulation monitored by BRET.
(C) Diffusivity states of receptor and βArr2 molecules. Trajectories (left) are after isoproterenol stimulation (10 μM; late).
(D and E) Estimated kon (D) and koff (E) values for β1AR, β2AR, and β2V2R-βArr2 interactions.
Data are mean ± SEM in (B) and median ± 95% confidence interval in (C)–(E). Results in (C) and (D) are statistically significant by Kruskal-Wallis test. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001 versus corresponding basal condition, and ++p<0.01, +++p < 0.001, ++++p < 0.0001 versus corresponding β1AR condition by t test with Bonferroni correction. ns, statistically not significant.