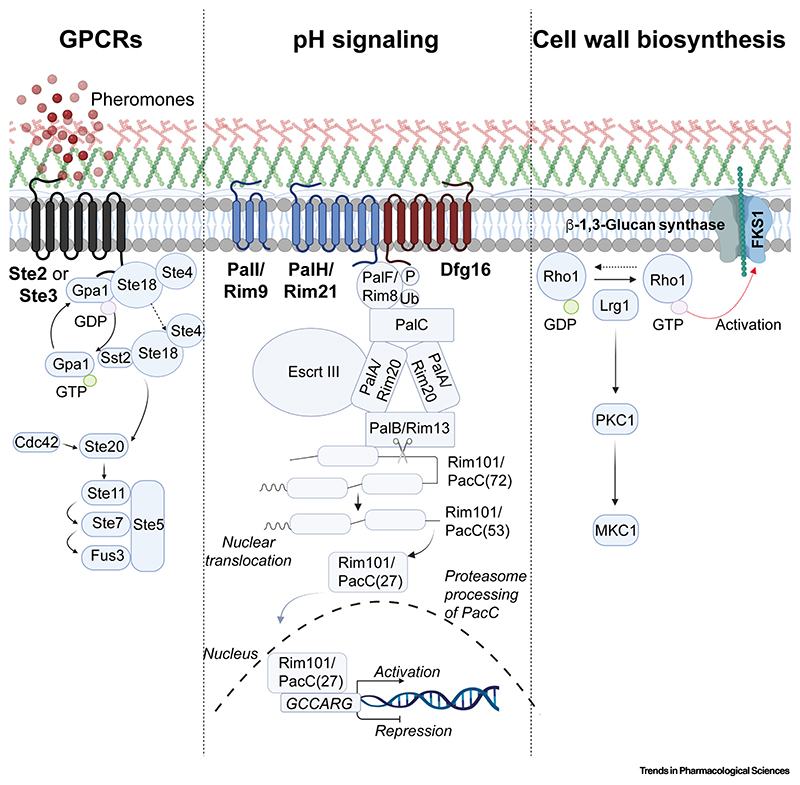
Figure 2. Signaling pathways of conserved fungal plasma membrane proteins required for virulence.
Activation of Ste2, a conserved pheromone-sensing class D GPCR (G protein-coupled receptor), results in stimulation of MAPK signaling and cell cycle arrest. The pH-sensing mechanism is highly conserved across many fungal pathogens and governs activation of the pH-responsive transcription factor Rim101/PacC which regulates adaptation to alkaline environments. The functionality of the pH-sensing mechanism also influences fungal susceptibility to various antifungals including echinocandins and 5-flucytosine (5FC). Rho1, a GTPase, is essential in several fungal pathogens and regulates cellular morphogenesis via mechanisms such as the activation of β-1,3-glucan synthase, and is a crucial component of the cell wall integrity pathway. Image created using BioRender.