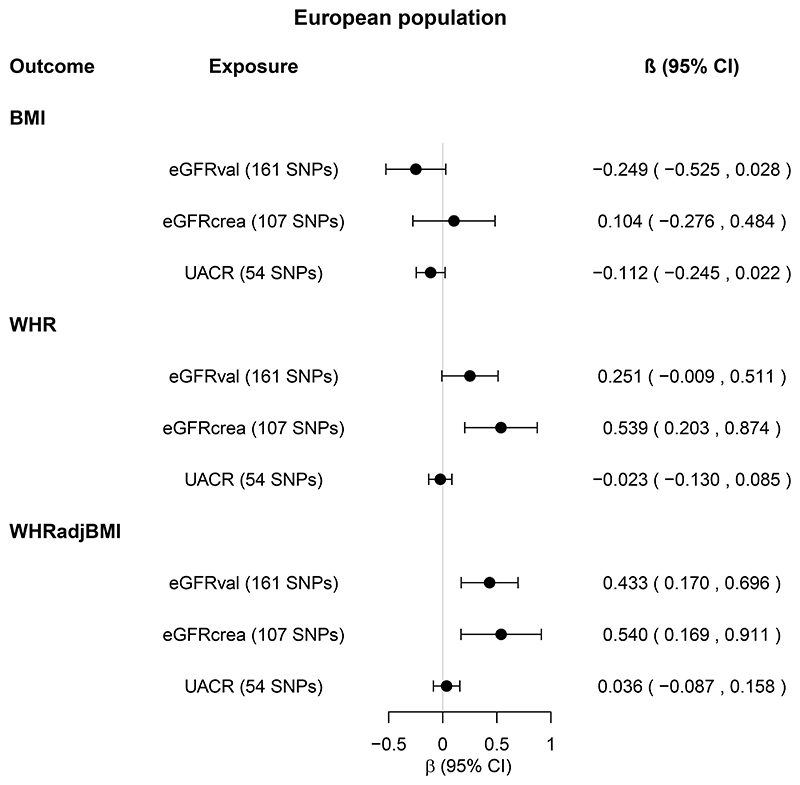
Figure 5. Total causal effects of kidney function on obesity in the European population.
Estimates (β coefficients and 95% confidence intervals [CIs]) are from the inverse variance weighted random-effects Mendelian randomization analysis, and expressed in log units per standard deviation increase in the relevant exposure.
Kidney function exposures from the CKDGen Consortium were eGFRval (estimated glomerular filtration rate based on creatinine and calculated by CKD-EPI equation, and validated by being associated with cystatin C and inversely associated with blood urea nitrogen [BUN]), eGFRcrea (eGFR based on creatinine and calculated by CKD-EPI equation, and validated by being inversely associated with BUN, N=567,460-1,004,040) and UACR (urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio, N=547,361). For each kidney function exposure, the number of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) included in the analysis is shown in parenthesis.
Obesity outcomes from the GIANT Consortium and UK Biobank combined were BMI (body mass index, N=795,624), WHR (waist-to-hip ratio, N=697,702), and WHRadjBMI (WHR adjusted for BMI, N=694,469). Sensitivity MR analyses are shown in Supplemental Tables 7-8.