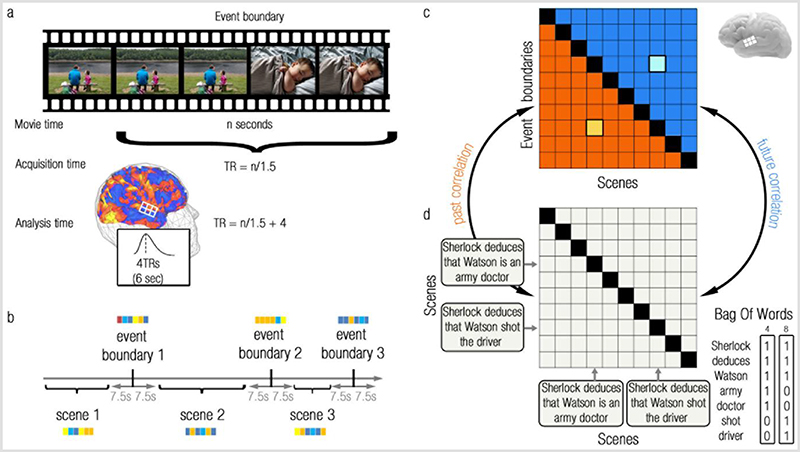
Figure 1. Analysis pipeline.
(a) Participants watched a movie/listened to a story while being scanned. We defined event boundaries as TRs in which scenes transitioned (TR=1.5 sec). We next shifted these TRs by 6 seconds (4 TRs) to account for the hemodynamic delay. (b) For each sphere in the brain, we extracted fMRI representations of event boundaries (black vertical lines). To separate the BOLD signals of event boundaries and scenes, we defined scene-representations as the average representation across all within-scene TRs that are 5 TRs (7.5 seconds) remote from adjacent event boundaries. (c) For each sphere, we created a similarity matrix by cross-correlating the representations of event boundaries and scenes. The lower/upper triangular parts of the matrix contained the similarities between event-boundary representations and the representations of preceding/following scenes (past/future parts of the matrix, orange/blue colours, respectively). We removed the main diagonal to measure only reactivation of temporally-remote scenes. Note that if similarities between event boundaries and scenes merely reflected scene-similarities, this similarity would be reflected in both the past and future parts of the matrix. For example, if the similarity between event boundary 8 and scene 4 (entry (8,4), bright orange) in fact reflected the similarity between scene 8 and scene 4, then the same similarity should be evident in the future part of the matrix (entry (4,8), bright blue). To control for this possibility, we defined a reactivation index as the difference between the means of the past and future parts of the matrix, thus cancelling out any symmetric scene-similarity effects. (d) Bag Of Words analysis. We represented each scene according to the occurrences of words, from across the entire narrative, that were used in that scene (illustrated for scenes 4 and 8). We then cross-correlated these scene-representations to create a context similarity matrix. Next, we correlated the past/future part of the neural similarity matrix with the past/future part of the context similarity matrix, respectively. Finally, we subtracted the future correlation coefficient from the past correlation coefficient, thus controlling for scene-similarities. See Methods for the variations of this method used for different datasets and analysis method.