Extended Data Fig. 10. Additional data for methodology.
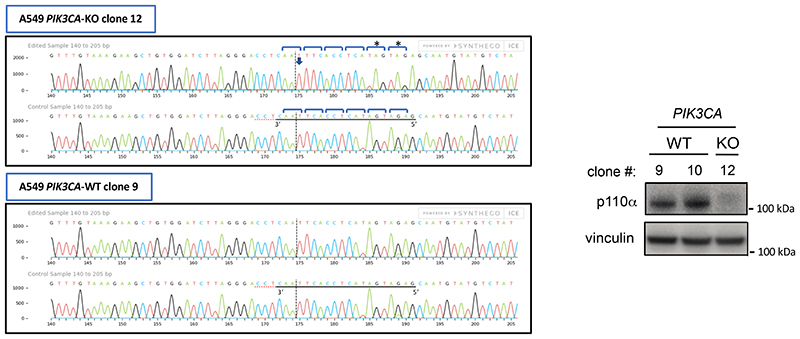
Left panel, Sanger sequencing of the genomic PIK3CA locus of A549 cell clones subjected to CRISPR/Cas9 gene-targeting. Lower traces: reference genomic PIK3CA sequence (wild-type), with the crispr RNA sequence underlined. Top traces: DNA sequence of CRISPR/Cas9 gene-targeted or control-edited A549 clones. The PIK3CA-KO clone 12 shows a +1 bp insertion (arrow), leading to frameshift and the generation of 2 consecutive premature stop-codons (asterisk) immediately downstream of the +1 bp insertion. Note that the first stop-codon occurs 80 bp upstream from the 3’ exon-exon junction and will therefore result in nonsense-mediated decay of the mRNA. The PIK3CA-WT clone 9 shows wild-type genomic DNA sequence. Right panel, Western blot for p110α using antibody CST#4255.