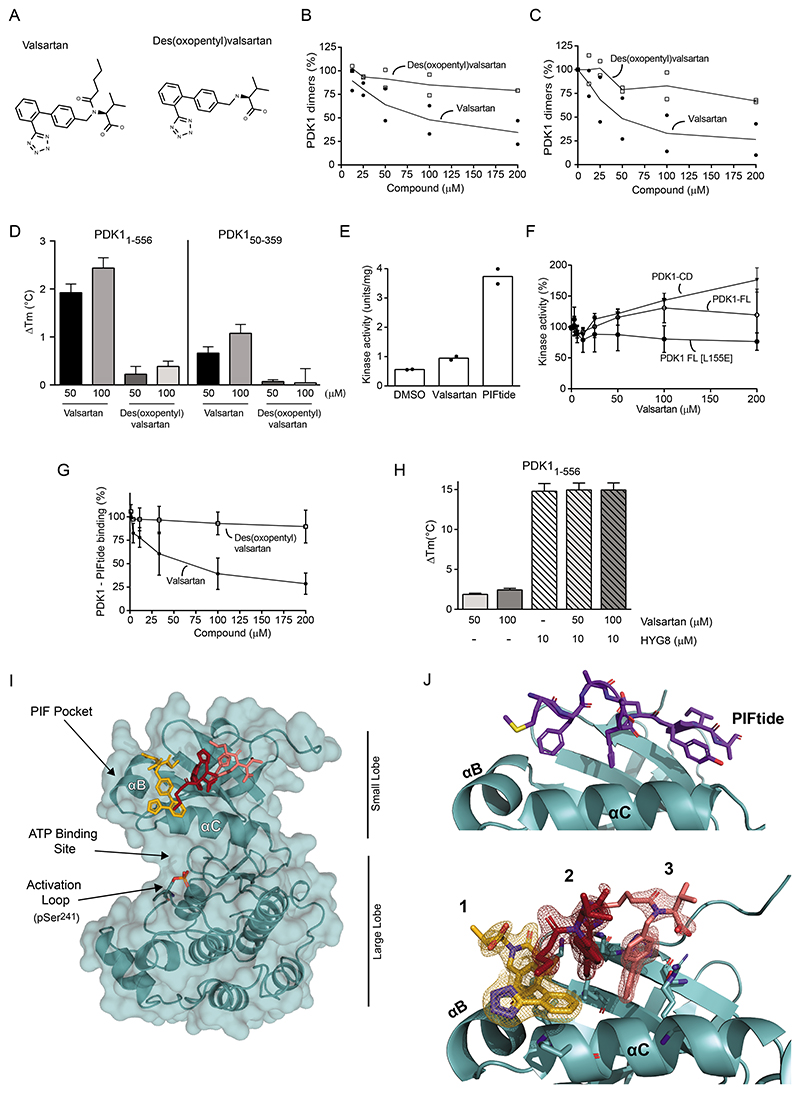
Fig. 5. Valsartan inhibits PDK1 dimerization by interacting with the PIF pocket of PDK1.
The AlphaScreen PDK1 dimerization assay (His-PDK11-556 and GST-PDK1360-556) was used to screen a compound library (Prestwick Chemical Library®) for small molecules that affect the interaction. (A) Chemical structures of the hit compound identified, valsartan, and the inactive related compound, des(oxopentyl) valsartan. (B and C) The effect of valsartan and des(oxopentyl) valsartan on the interaction between His-PDK11-556 and GST-PDK11-556 (B) and on the interaction between His-PDK11-556 and GST-PDK1360-556 (C) was assessed. N=2 independent experiments. (D) Thermal stability of PDK11-556 and PDK150-359 in the presence of valsartan and des(oxopentyl) valsartan. N=3 independent experiments. (E) The effect of DMSO, valsartan (200μM) and PIFtide (2μM) on the specific activity of the catalytic domain of PDK1 (PDK11-359). N=2 independent experiments. (F) The effect of valsartan was tested on the activity of the catalytic domain of PDK1 (PDK11-359; catalytic domain, CD), on WT full-length PDK1 (PDK11-556; FL) and full-length PDK1 mutated at a central residue in the PIF pocket, L155E (PDK1 FL [L155E]). N=3 independent experiments. (G) Effect of valsartan and des(oxopentyl) valsartan on the interaction between GST-PDK11-556 and biotin-PIFtide as assessed with AlphaScreen technology. N=3 independent experiments. (H) Effect of valsartan on the thermal stabilization of PDK11-556 by HYG8. N=3 independent experiments. (I) Crystal structure of PDK1 in complex with valsartan (PDB: 8DQT). (J) Magnified view of the PIF pocket of PDK1 depicting the PIFtide binding mode (top) (PDB: 4RRV (31)) and of the same orientation of the pocket in complex with the three molecules of valsartan. The 2mFo-DFc electron density map of the valsartan molecules is shown at the σ=1.0 level (bottom).