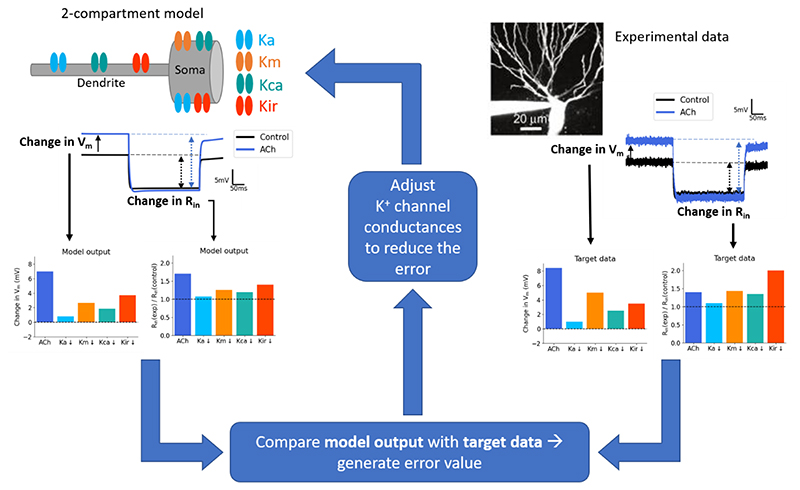
Figure 1. Optimisation of potassium conductances in 2-compartment model.
Potassium channel conductance parameters were optimised by fitting to experimental data (from Makara and Magee (2013) and Sun and Kapur (2012)) measuring the change in membrane potential and input resistance after inhibiting the relevant potassium conductance. The error represented the difference between the model output and the target data which then fed back into the optimisation algorithm to adjust the potassium conductances. This cycle was repeated many times until the error was minimised. The bar plots shown represent the target experimental data used (right) and the final optimised output in the model (left). Neuron image adapted from Makara and Magee (2013). Vm = resting membrane potential; Rin = input resistance; Ka = A-type potassium channel, Km = M-type potassium channel, Kca = SK channel, Kir = GIRK channel.