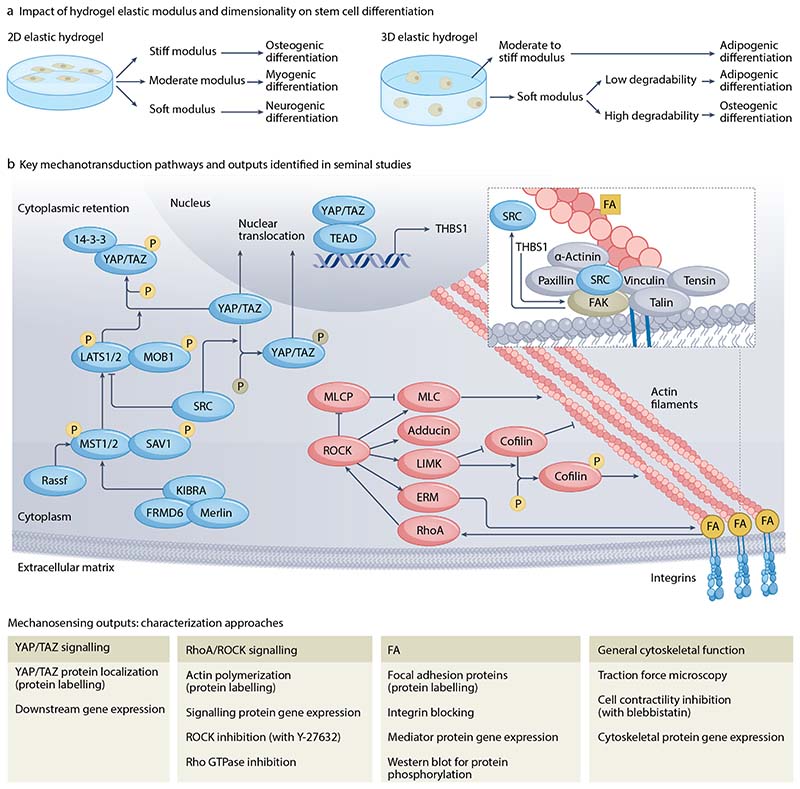
Figure 5. Hydrogels for directing stem cell fate by engaging mechanotransduction pathways.
a) Hydrogel modulus and dimensionality impact cellular mechanotransduction. Their impact on promoting human mesenchymal stem cell (hMSC) differentiation is highlighted. Hydrogels can be designed with specific mechanical properties to promote stem cell fate specification. b) Seminal studies with hMSCs, amongst other cell types, have elucidated that mechanotransduction is mediated, in part, by YAP/TAZ and RhoA/ROCK signaling, focal adhesion formation and more generally the cytoskeleton. Key pathways are noted along with approaches for characterizing them. 14-3-3, tyrosine 3-monooxygenase/tryptophan 5-monooxygenase activation protein; ERM, ezrin/radixin/moesin protein family; FA, focal adhesion complex; FAK, focal adhesion kinase; FRMD6, FERM (4.1-ezrin-radixin-moesin) domain-containing protein 6; KIBRA, kidney and brain expressed protein; LATS1/2, serine/threonine-protein kinase 1/2; LIMK, LIM domain kinase; MLC, myosin light chain; MLCP, myosin light chain phosphatase; MOB1, monopolar spindle-one-binder 1; MST1/2, macrophage stimulatory protein 1/2; P, phosphate group (indicates phosphorylation and dephosphorylation); Rassf, Ras association domain-containing family; RhoA, Ras homolog family member A; ROCK, Rho-associated protein kinase; SAV1, protein salvador homolog 1; SRC, proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src; TAZ, transcriptional co-activator with a PDZ-binding motif; TEAD, transcriptional enhancer factor TEF; THBS1, thrombospondin 1 (gene), YAP, yes-associated protein.