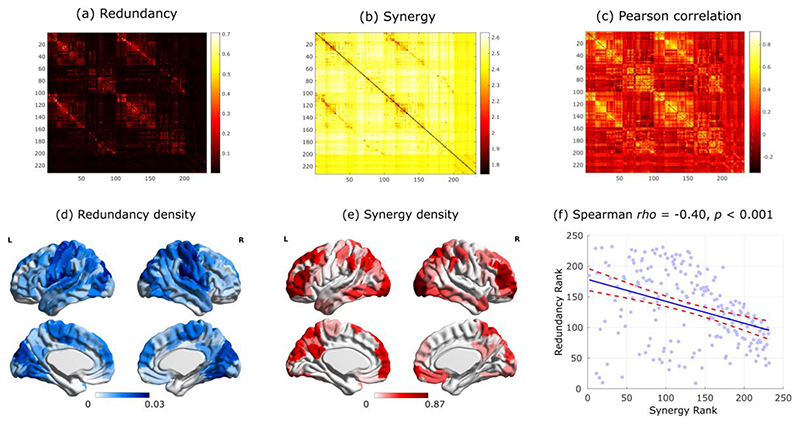
Extended Data Fig. 1. Synergistic and redundant interactions in the brain.
(a-c) Group average matrices of pairwise functional interactions between brain regions of the Schaefer-232 atlas, quantified by (a) redundancy; (b) synergy; (c) traditional functional connectivity (Pearson correlation). (d) Mean regional density of redundant interactions, after thresholding the group-average redundancy matrix to retain the 5% strongest edges, for display purposes. (e) Mean regional density of synergistic interactions, after thresholding the group-average synergy matrix to retain the 5% strongest edges, for display purposes. (f) Spearman correlation (two-sided CI: [-0.51, -0.28]) between synergy vs. redundancy ranks across cortical regions.