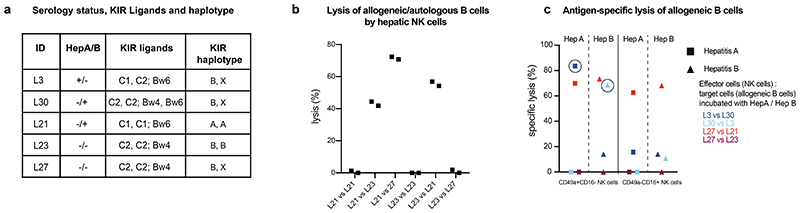
Figure 4. Antigen-specific killing by CD49a+CD16- hepatic NK cells of allogeneic target cells is dependent on KIR receptor-ligand match.
a, Serology status, KIR Ligands and KIR haplotype of five tested individuals. b, Percentage of lysis of allogeneic/autologous B cells by hepatic NK cells as indicated. B cells were not incubated with antigens. Data points depict two independent replicates of each condition. c, Percentage of specific lysis of allogeneic B cells after incubation with hepatitis A/B proteins by CD49a+CD16-/CD49a-CD16+ hepatic NK cells. Circled data points indicate NK cell killing that cannot be explained by their KIR pattern. Data are presented as mean specific lysis ± SD of triplicates of each individual.