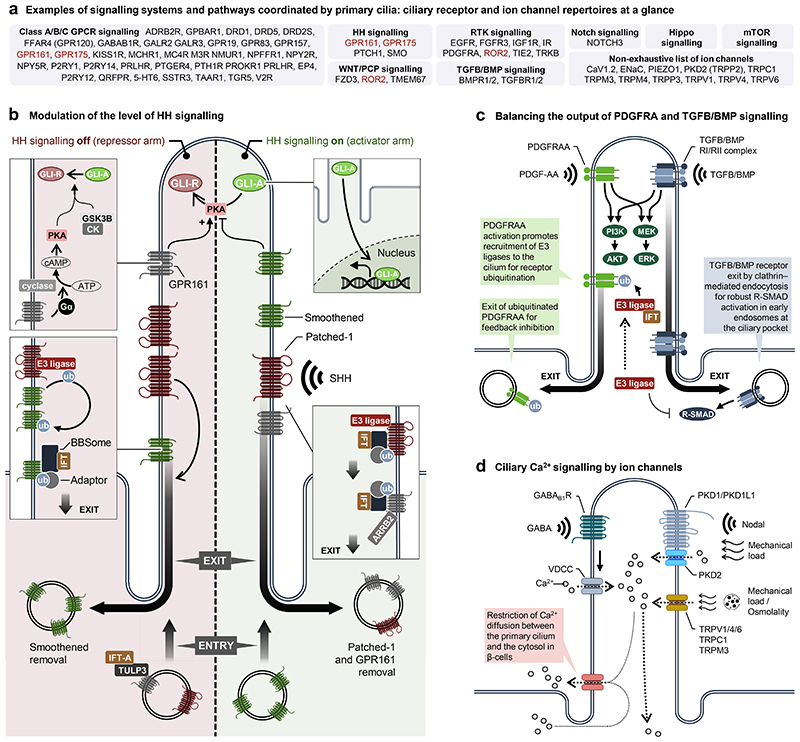
Figure 2. Overview of signalling pathways coordinated by primary cilia.
a, Overview of receptors and ion channels in ciliary signalling pathways. Receptors in red are listed twice, as they can be categorized in more than one signalling system. b, Overview of Hedgehog (HH) signalling. In the absence of sonic hedgehog (SHH) (in the repressor arm of HH signalling), the receptor patched-1 (PTCH1) is enriched in the ciliary membrane, preventing ciliary enrichment of smoothened (SMO) through WWP1 (E3-ligase)-mediated ubiquitination and ciliary exit by retrograde IFT. The class A GPCR, GPR161, is targeted to the cilium by tubby-like protein 3 (TULP3) and IFT-A to activate adenylate cyclases via G-proteins (Gα), leading to increased ciliary levels of cAMP. cAMP activates protein kinase A (PKA), which in complex with glycogen synthase kinase 3 β (GSK3β) and casein kinases (CK) promotes the limited proteolytic cleavage of full-length and activator versions of GLI2/3 transcription factors (GLI-A) into their repressor form (GLI-R). In the presence of SHH (in the activator arm of HH signalling), PTCH1 and GPR161 exit the cilium, allowing enrichment of ciliary SMO, which promotes formation of GLI-A. Exit of PTCH1 and GPR161 similarly relies on their ubiquitination and removal by BBSome-assisted retrograde IFT; GPR161 ubiquitination being controlled at the level of beta-arrestin 2 (ARRB2). Both GLI-A and GLI-R translocate from the cilium into the nucleus to induce and repress transcriptional activation of HH target genes, respectively. c, Overview of ciliary control of platelet-derived growth factor α (PDGFRα) and transforming growth factor β (TGF-β)/bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signalling. Following activation of PDGFRα and downstream signalling via PI3K-AKT and MEK1/2-ERK1/2 pathways, E3 ligases of the CBL family ubiquitinate the receptor for internalization and feedback inhibition. TGFB/BMP signalling operates in the cilium via both canonical (R-SMAD) and non-canonical (e.g. PI3K-AKT and MEK1/2-ERK1/2 pathways). Robust canonical signalling relies on ciliary exit of activated TGFB receptors to activate R-SMADs, which are inhibited by E3-ligase SMURF1 at the ciliary pocket. d) Examples of stimulation modes (chemosensation, mechanosensation and osmolality) for ciliary Ca2+ signalling regulated by GPCRs and ion channels. Please see main text for further details. Abbreviations Ub: ubiquitination.