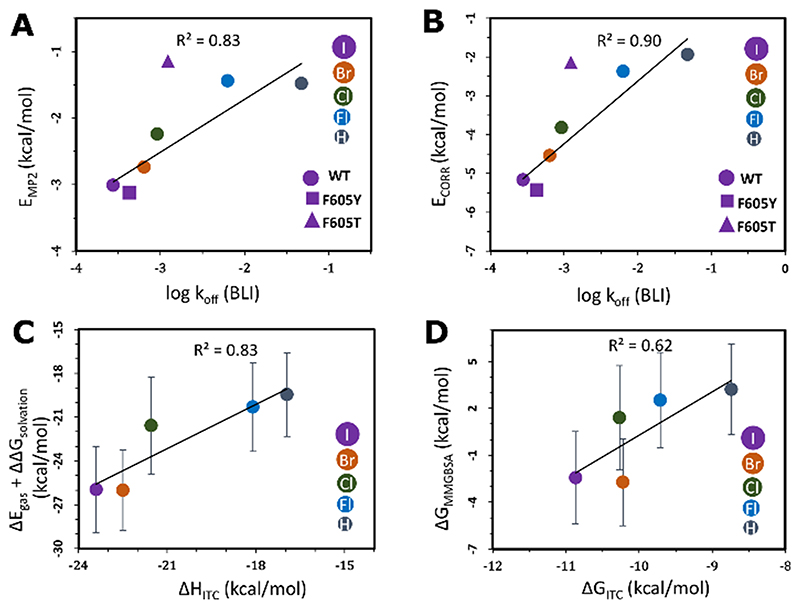
Figure 5. Correlation of the calculated binding free energies with experimental parameters for the halogen–gatekeeper interaction.
A) Second-order Møller–Plesset interaction energies (EMP2) and B) the second-order correlation correction energy terms (ECORR) between the TU derivatives and the gatekeeper residues versus the BLI koff values. The linear fits and correlation coefficients (R2) were computed by omitting the outlier F605T mutant. The experimental error bars are smaller than the size of the data points. Comparisons of C) MMGBSA internal and solvation contributions (ΔEgas+ΔΔGsolvation) versus the ITC enthalpies (ΔHITC) and D) the MMGBSA binding free energies (ΔGMMGBSA) versus the ITC binding free energies (ΔGITC) of the interactions between haspin and TU derivatives. Some ΔGMMGBSA values are positive as they only include translational and rotational entropic terms and do not include vibrational and conformational entropy contributions.